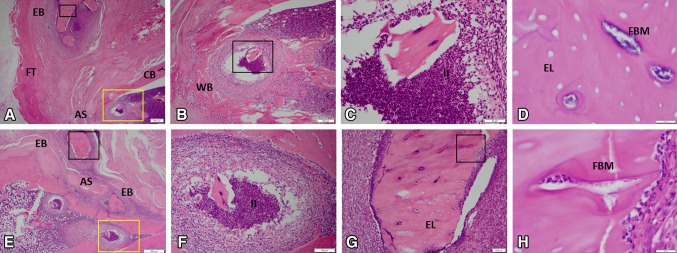
Fig. 4A–H.
The histological features of ectopic bone formation in MRSA-treated rats at 12 weeks are shown in A–H (A, Stain, hematoxylin and eosin; A original magnification, × 1.25; B, original magnification, × 4, yellow boxed region in A; C, original magnification, × 20, black boxed region in B; D, original magnification, × 100, black boxed region in A; E, original magnification, × 2; F, original magnification, × 10, yellow boxed region in E; G, original magnification, × 10, black boxed region in E; H, original magnification, × 10, black boxed region in G). For detailed evaluation, images of six selected regions at higher magnification are shown. In the medullary space and soft tissue, there is evidence of chronic inflammation, neutrophil infiltration, purulent infection, osteomyelitis, and necrotic ectopic bone as indicative of empty osteocytic lacunae containing bacterial microcolonies. AS = amputation site; CB = cortical bone; EL = empty lacunae; EB = ectopic bone; FBM = foci of bacterial microcolonies; FT = fibroblastic tissue; II = intramedullary infection; WB = woven bone.