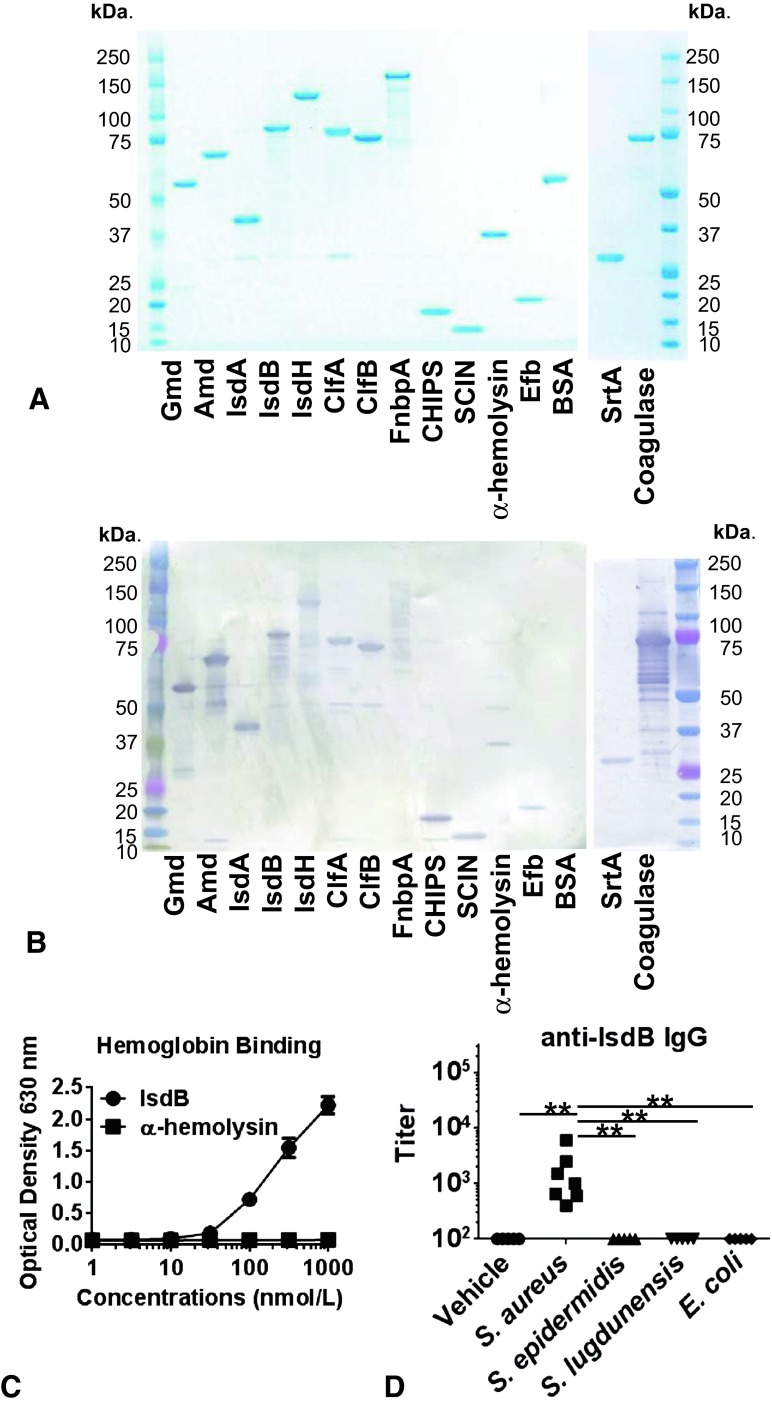
Fig. 1A–D.
A validation of recombinant S aureus antigens is shown. (A) The 14 recombinant proteins (1μg) and Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a control protein were separated in 4% to 12% gradient sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gels and stained with Coomassie blue, showing that the dominant band in each lane is consistent with the predicted molecular weight of the tagged full-length protein. (B) Identical SDS-PAGE gels were immunoblotted using pooled high-titered human sera as the primary antibody and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat-antihuman immunoglobulin G (IgG) as the secondary. The immunoreactivity to the dominant band for each S aureus antigen can be seen. (C) Functional assays specific for each antigen were run to show that each antigen possessed the documented activity of the native protein. A representative example in which the binding of recombinant histadine (His)-IsdB-biotin to immobilized human hemoglobin was detected using a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin ELISA is shown. Histadine-α-hemolysis-biotin was used as a negative control. (D) Balb/c mice were challenged with a vehicle, S aureus, S epidermidis, S lugdunensis, or E coli at Days 0 and 28 and sera were collected at Day 42. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 with Kruskal-Wallis test. IgG titers against the 14 recombinant antigens were determined by ELISA and data for anti-IsdB titer are presented as a representative example, as infection with other species did not elicit IgG cross-reactive with the S aureus antigens. Gmd = glucosaminidase; Amd = aminidase; IsdA = iron-regulated surface determinant protein A; IsdB = iron-regulated surface determinant protein B; IsdH = iron-regulated surface determinant protein H; ClfA = clumping factor A; ClfB = clumping factor B; FnbpA = fibronectin binding protein A; CHIPS = chemotaxis inhibitory protein of Staphylococcus aureus; SCIN = staphylococcal complement inhibitor; Efb = extracellular fibronectin-binding protein; BSA = bovine serum albumin; SrtA = sortase A.