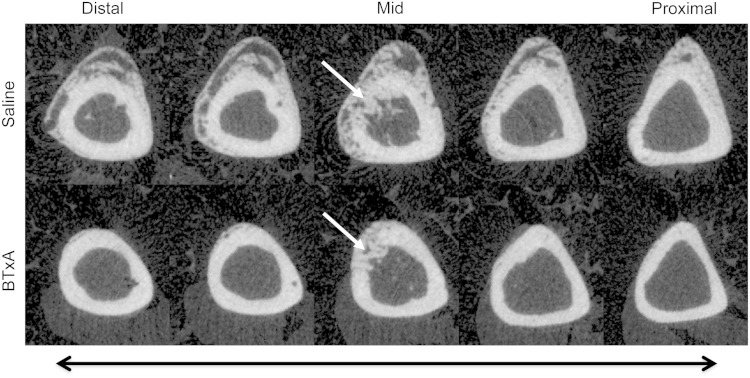
Fig. 2.
Serial micro-CT images along a 2-mm region of the tibial diaphysis in a saline-treated mouse (“saline,” top) demonstrates exuberant osteogenesis both distal and proximal to the surgically created bone defect. Furthermore, it can be seen that the cortical defect is being repaired by calcifying tissues (white arrow in the middiaphyseal image). In contrast, transient paralysis of the calf muscle induced by BTX (“BTxA,” bottom) inhibited osteogenesis along the entire diaphyseal length without affecting calcifying tissues adjacent to or within the injury itself.