FIG 2.
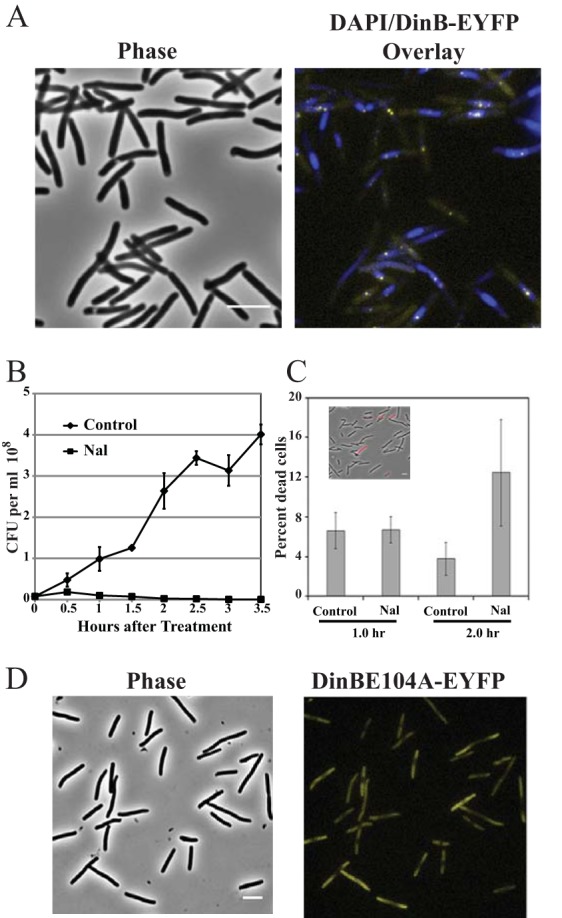
Localization of Pol IV and cell survival after Nal exposure. (A) Phase-contrast and phase plus fluorescence overlay images of DinB-12L-EYFP localization. Strain PFB243/pPFB913 was grown in LB broth plus antibiotics at 37°C to mid-exponential phase (OD600 = 0.5), treated with 40 μg/ml Nal, and incubated for a further 1 h. The cells were then stained with DAPI and visualized for DinB-EYFP foci. The DinB-EYFP (yellow) foci were associated with DAPI-stained nucleoids (blue). (B) Colony-forming ability of Nal-treated cells. Strain PFB243/pPFB913 was grown as described for panel A, and half the culture was treated with Nal. Samples were withdrawn from the cultures at the indicated time points and plated for CFU. Shown are the means ± SEM of 3 cultures (some error bars are smaller than the symbols). (C) Propidium iodide staining of Nal-treated cells to estimate cell viability based on membrane integrity. After exposure to Nal as for panel A, samples were washed and suspended at 10× in saline, stained with propidium iodide, and imaged. Shown are the mean percentages ± SEM of the cells stained with propidium iodide based on 2 or 3 fields examined with 125 to 710 cells counted per field; the inset shows a phase-contrast image overlaid with a fluorescence image (red). (D) Failure of an active-site mutant Pol IV (DinBE104A-EYFP) to form fluorescent foci. Strain PFB243/pPFB1173 was treated with Nal as for panel A. Shown are the phase-contrast and fluorescence images of DinBE104A-EYFP localization. Scale bars = 5 μm.
