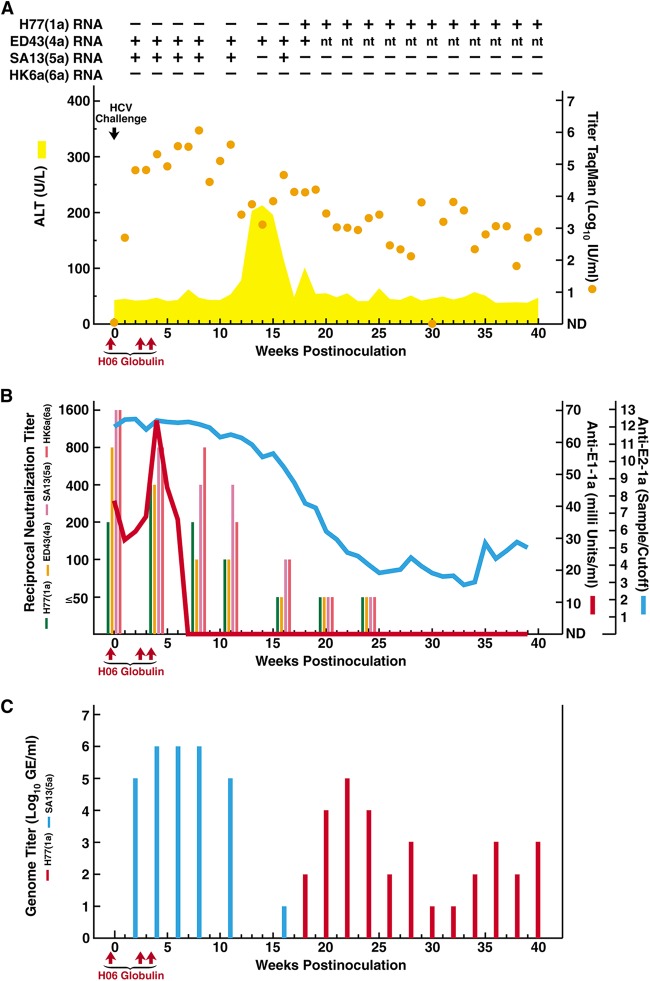
FIG 1.
Course of hepatitis C infection in a chimpanzee loaded with polyclonal genotype 1a immunoglobulins and challenged with homologous and heterologous HCV strains. Chimpanzee CHA5A009, who was naive for HCV, as well as for other hepatitis viruses, was infused intravenously with immunoglobulins (H06), prepared from plasma obtained from patient H with chronic HCV, at the time points indicated with red arrows; the first infusion was 24 h before HCV challenge. The intravenous challenge (indicated by a black arrow) was 100 chimpanzee infectious doses of each of the HCV strains (with genotype in parentheses) H77(1a), ED43(4a), SA13(5a), and HK6a(6a). (A) Serum samples were tested for HCV RNA by in-house RT-nested PCR with strain-specific primers (Table 1): +, positive; −, negative; nt, not tested. The estimated log10 HCV RNA titers (international units per milliliter), determined in an in-house TaqMan assay (orange dots), were plotted against time; a single sample below the detection limit of ∼10 IU/ml is shown as “not detected” (ND). The area shaded yellow shows serum ALT (units per liter). Results of samples collected after week 40, at weeks 50 and 56, are only referred to in the text. (B) Anti-HCV antibodies against E1 (red line) and E2 (blue line) were detected in serum by 1a-specific ELISAs. The serum neutralizing reciprocal antibody titers, determined in HCVpp assays using H77, ED43, SA13, and HK6a pseudoparticles, are shown in colored bars as indicated. (C) The serum H77(1a) and SA13(5a) genome titers, determined by in-house RT-nested PCR with strain-specific primers (Table 1) on 10-fold serially diluted RNA, are indicated by red and blue bars, respectively.