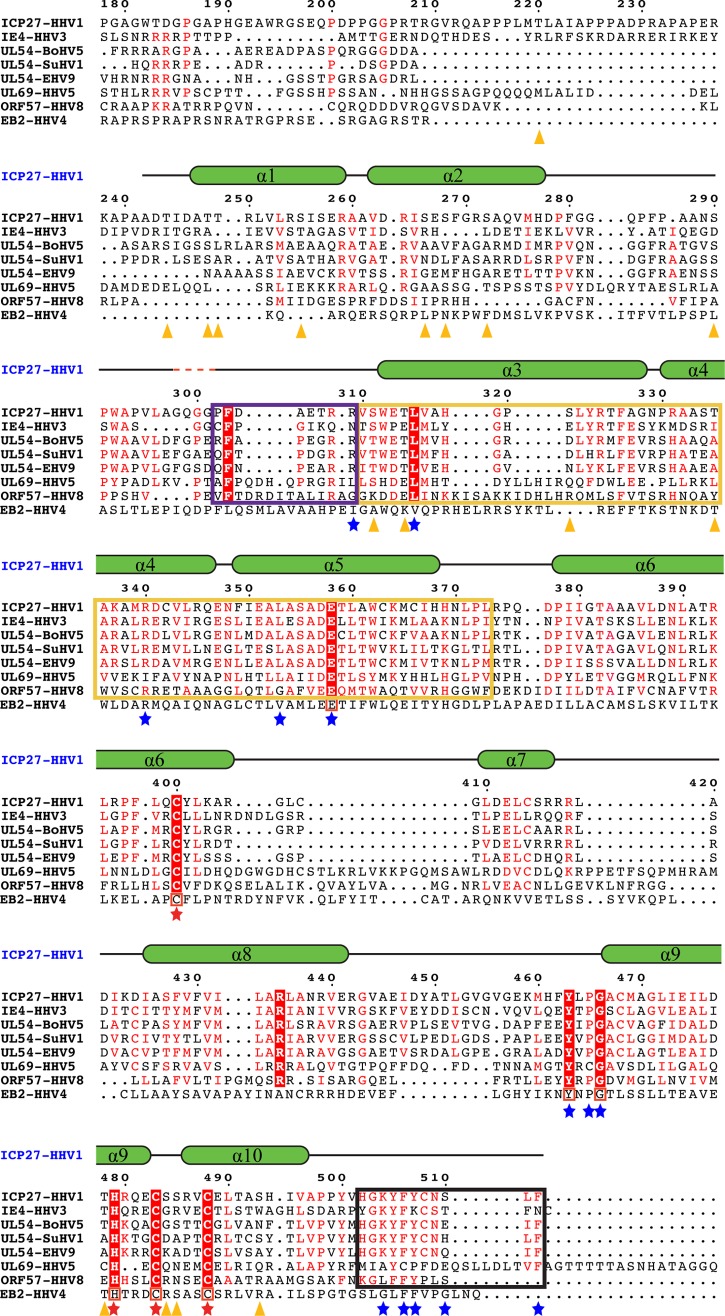
FIG 5.
Comparison of ICP27 with its homologs. ICP27-CTD (HHV1) sequence is aligned with its various homologs from the alphaherpesvirus family (IE4 from HHV3, UL54 from bovine herpesvirus 5 [BoHV5], UL54 from suid herpesvirus 1 [SuHV1], and UL54 from equine herpesvirus 9 [EHV9]), the betaherpesvirus family (UL69 from HHV5), and the gammaherpesvirus family (ORF57 from HHV8). Secondary structural elements of ICP27-CTD are drawn above the sequences as green α-helices with black-lined loops, with a red dashed line showing the position of the four missing residues. Residues conserved in all sequences are highlighted in red boxes with a white font; residues with similar sequences are highlighted in a red font. Residues involved in the zinc-binding motif of ICP27-CTD are marked with a red star. A black box is used to indicate the residues forming the C-tail, a yellow box indicates the hydrophobic pocket region, and a purple box indicates the flexible cap region as observed in ICP27-CTD structure. Residues involved in key interactions between the hydrophobic pocket and the C-tail are marked with a blue star. Orange triangles indicate the positions of residues phosphorylated in the in vitro assay and analyzed by mass spectrometry. Multiple sequence alignment was performed using CLUSTAL Omega, and sequence similarities were rendered using ESPript3. The sequence of ICP27 homolog from HHV4, i.e., the EB2 protein, is manually aligned to the above multiple sequence alignment. The conserved residues are boxed in red.