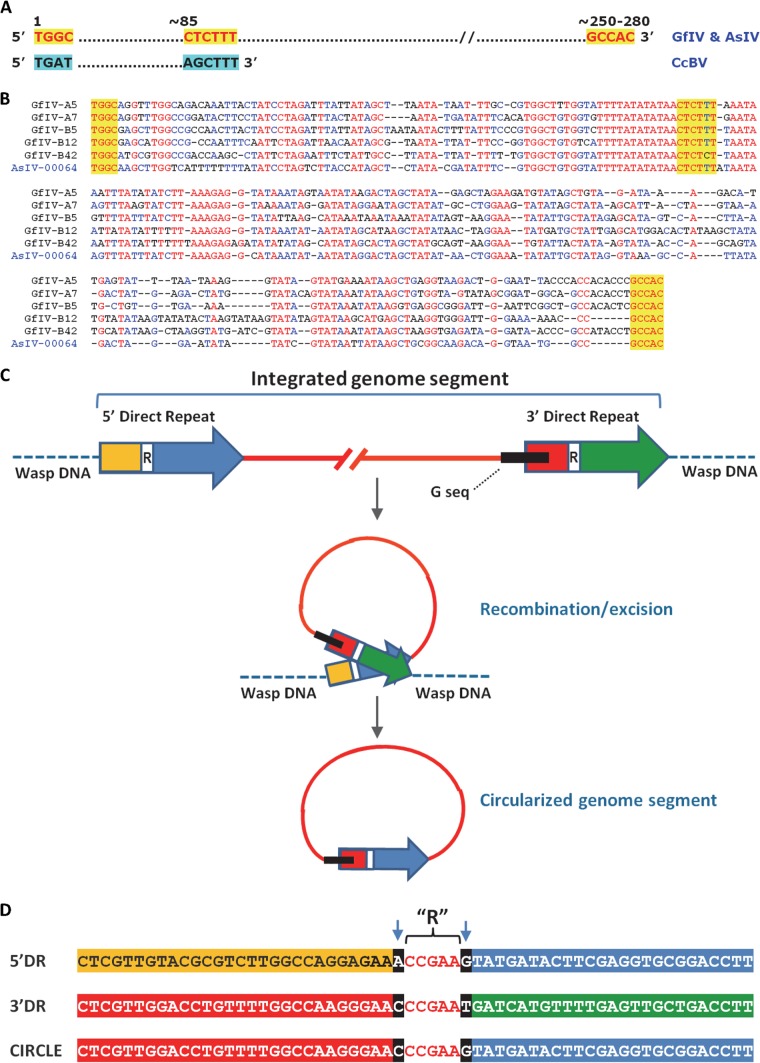
FIG 5.
G sequences and direct repeats within chromosomal copies of GfIV genome segments and their proposed role in genome segment excision/circularization. (A) Three recognizable motifs (shaded in yellow) within an ∼250- to 280-bp region (G sequence) conserved among packaged GfIV and AsIV genome segments are shown; below are shown BV motifs resembling those found in GfIV and AsIV, including the DRJ motif, AGCTTT. (B) Alignment of the G sequences of the five GfIV genome segments examined here. A sample from AsIV is also included for comparison. Sequences shaded in yellow are those highlighted in panel A. (C) Schematic representation of the direct repeats (DRs) and associated G sequence found in proviral homologs of GfIV genome segments, along with a model for their involvement in segment excision/circularization. The DRs are represented by an arrow at each end of the integrated segment. Each DR contains a recombination region (indicated by an R and white box) whose position varies among segments (Table 3). The G sequence is represented by a black box. For genome segment excision, the DRs come in close proximity to allow recombination through the recombination regions; following recombination and excision, the circle contains a single, hybrid DR whose 3′ and 5′ ends come from the 5′ DR and the 3′ DR of the proviral genome segment, respectively. The exact role of the G sequence in this process, if any, is unclear at this stage. (D) Identification of the R region, using genome segment A7 as an example. The full 5′ and 3′ DRs are 313 and 312 bp long, respectively (Table 3); only their central portion is shown here. The R region was identified by aligning the two DRs and the homologous portion of the corresponding circle. The R region displayed perfect sequence identity among the three aligned sequences, while sequence variation was observed on either side of it (arrows). This sequence variation enabled identification of DR regions retained in the circle following recombination (the color scheme is the same as that shown in panel C).