FIG 1.
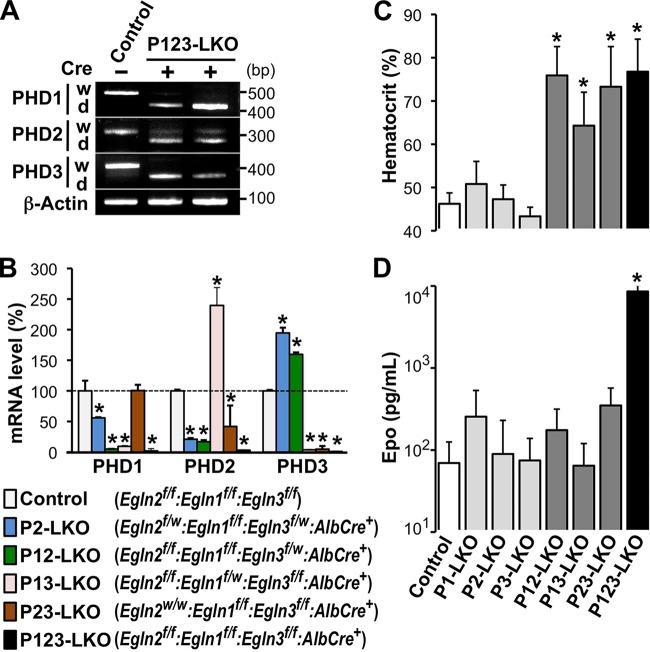
Liver-specific knockout of multiple PHD isoforms causes polycythemia. (A) RT-PCR was performed on livers from P123-LKO (Egln2f/f:Egln1f/f:Egln3f/f:AlbCre+ genotype) or control (Cre− Egln2f/f:Egln1f/f:Egln3f/f genotype) mice. Then, the PCR products were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis to detect the expression of longer and shorter transcripts from the normal (w) and targeted (d [deletion of the exon encoding the catalytic domain of each PHD isoform]) alleles, respectively. β-Actin was used as an internal control. (B) Average expression levels of PHD isoforms in the livers of the indicated genotype mice were measured by RT-qPCR. The values are averages for 3 to 5 mice in each group, with error bars indicating standard deviations (SD). *, P < 0.01 compared to the expression levels in the control mice, which are set at 100%. (C and D) Average hematocrit (C) and Epo concentration (D) in peripheral blood samples from PHD mutant mice at 8 to 19 weeks after birth. The values are averages for 4 to 12 mice in each group, with error bars indicating SD. *, P < 0.01 compared to the levels in the control mice.