FIG 2.
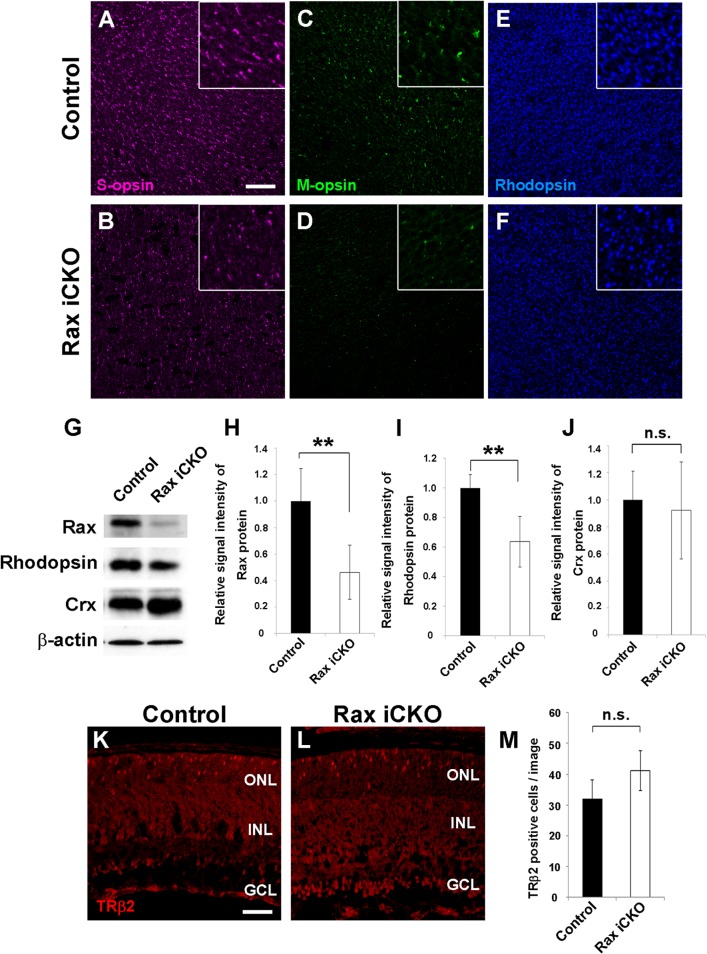
Expression of opsin genes decreases in the Rax iCKO mouse retina. (A to F) Whole-mount retinas from control and Rax iCKO (P4 → P8) mice were immunostained with antibodies against S-opsin (magenta) (A and B), M-opsin (green) (C and D), and rhodopsin (blue) (E and F). (Insets) S-opsin-, M-opsin-, and rhodopsin-positive cells at high magnification. Bar, 50 μm. (G to J) Comparison of photoreceptor protein levels in control and Rax iCKO (P4 → P8) mouse retinas. (G) Western blots of Rax, rhodopsin, and Crx in the retina are shown. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (H to J) The signal intensities of the Rax, rhodopsin, and Crx proteins, respectively, are shown. Data are means ± SDs (n = 3). **, P < 0.01 by Student's t test; n.s., not significant by Student's t test. (K to M) The number of cone photoreceptor cells was unaltered in the Rax iCKO (P4 → P8) mouse retina. Retinal sections from control (K) and Rax iCKO (P4 → P8) (L) mice were immunostained with an anti-TRβ2 antibody (rabbit; red), a marker for developing cone photoreceptor cells. Bar, 50 μm. (M) The number of TRβ2-positive cells is shown. Data are means ± SDs (n = 4). n.s., not significant by Student's t test. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer;.