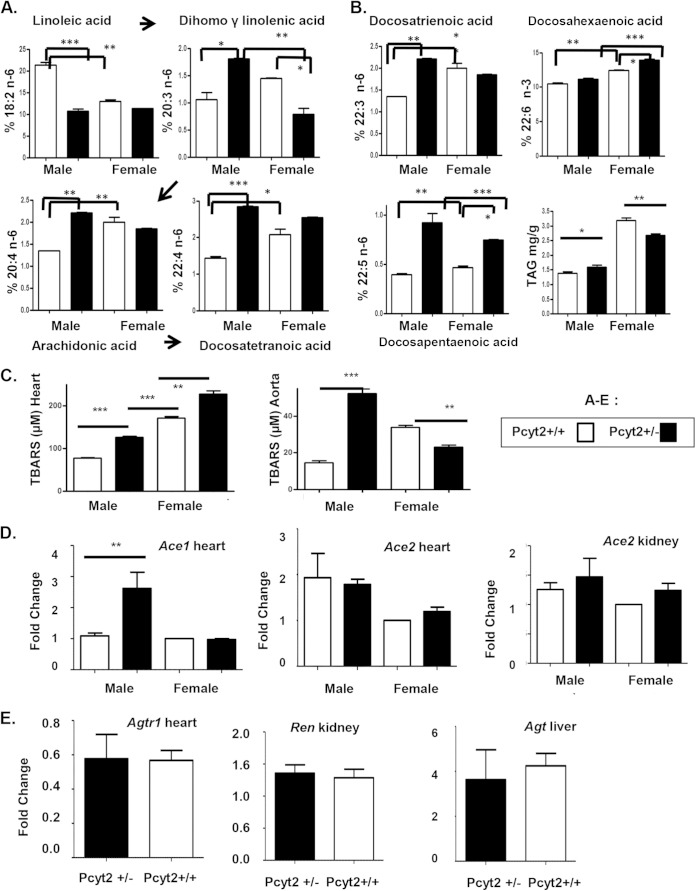
FIG 7.
Accumulation of arachidonic acid and long-chain n-6 PUFAs in Pcyt2+/− male heart. (A) Desaturation and elongation of the essential 18:2n-6 PUFA linoleic acid are sexually dimorphic and more active in wild-type female heart than in wild-type male heart (white bars). The production of arachidonic acid (20:4n-6) and longer-chain n-6 PUFAs from linoleic acid (18:2n-6) is upregulated only in Pcyt2-deficient male hearts (black versus white bars). (B) Cardiac levels of very-long-chain n-6 and n-3 PUFAs and total triglycerides also show sexual dimorphism and are elevated in wild-type female hearts (white bars). The level of docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3) additionally is increased only in Pcyt2+/− female heart. (C) ROS production is increased in both male and female Pcyt2+/− hearts, while in the aorta, ROS production is specifically increased in Pcyt2+/− males, showing male-specific vascular oxidative stress in Pcyt2 deficiency. (D and E) Pcyt2+/− male-specific overexpression of the AceI gene in the heart, with no differences in the rest of the renin-angiotensin system, i.e., Ace2 (heart and kidney), angiotensinogen (Agt) (liver), renin (Ren kidney), and angiotensin receptor (Agtr1) (heart). Values are means ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.