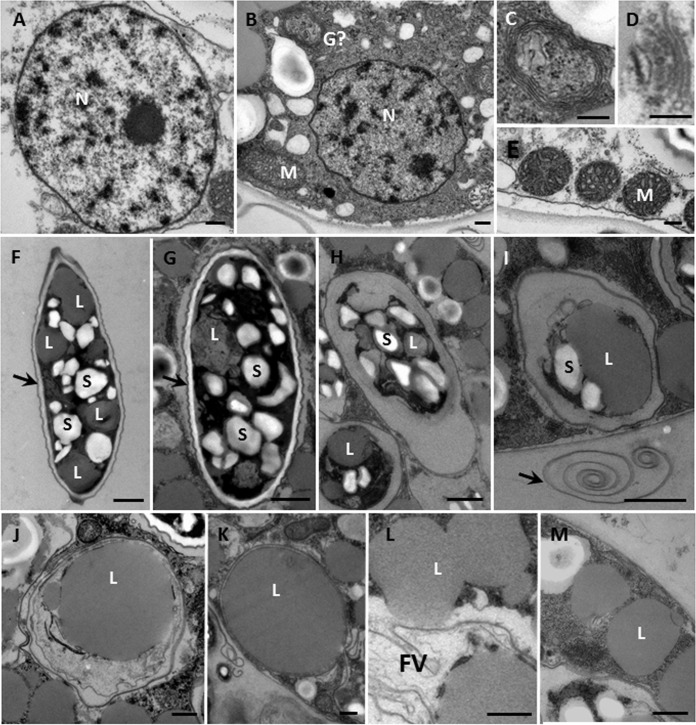
FIG 5.
Transmission electron microscopy. (A) Nucleus (N) of a digestive cyst; detail of Fig. 4A showing the central nucleolus. (B) Nucleus of another digestive cyst, with a mitochondrion (M) and a membranous structure (perhaps a Golgi body) (G). (C) Detail of the membranous structure in panel B. (D) Golgi apparatus; dictyosome with 5 sacs. (E) Mitochondria of trophozoite with tubulovesicular cristae. (F) Live Scenedesmus cell, with intact cell wall (arrow), lipid droplet (L) (average size, 1.2 μm by 1.2 μm), and starch particles (S). (G) Newly ingested intact algal cell in a food vacuole with intact cell wall (arrow). (H) Ingested prey cell in which the wall is breaking down. (I) Food vacuole with only starch and lipid; the arrow indicates some algal cell wall materials outside the amoeba. (J) Lipid droplet measuring 2.2 μm by 2.2 μm in a food vacuole. (K) Food vacuoles containing only a lipid droplet measuring 2.8 μm by 3.4 μm. (L) Detail of Fig. 4B suggesting that lipid is being released from a food vacuole (FV). (M) Lipid droplets near the cell surface. Scale bars = 0.2 μm (A to E), 1 μm (F to I), and 0.5 μm (J to M).