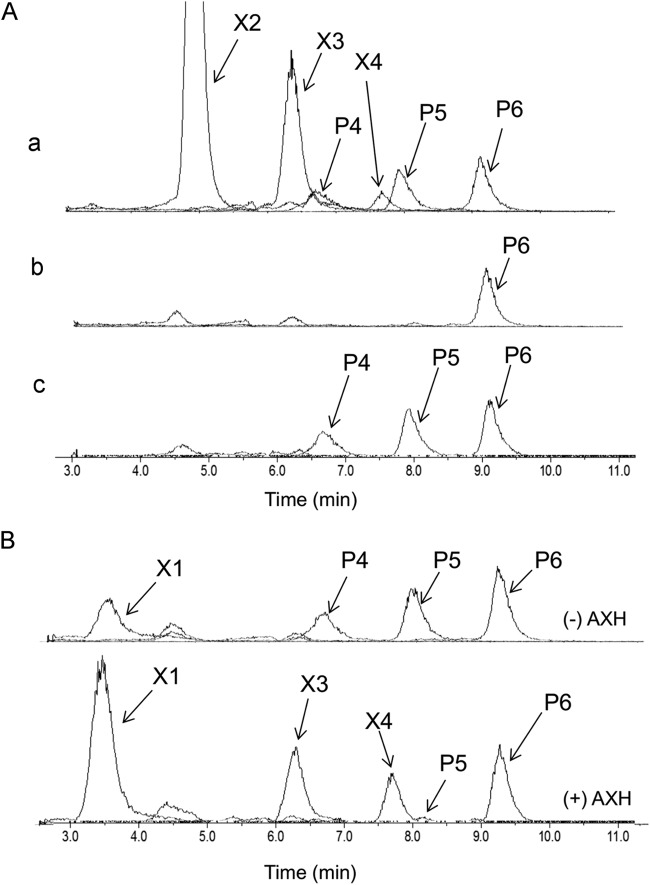
FIG 5.
Comparison of substrate utilization range of C. glutamicum recombinant strains. Strain X1EFGD and strain X1D were first grown aerobically to late log phase in A medium containing 40 g liter−1 of glucose and then inoculated to an initial OD610 of 0.5 into A medium containing 2.5 g liter−1 of xylooligosaccharide mixture. (A) Culture medium of the recombinant strains was analyzed by LC-ESI-MS at 0 h (a), at 30 h for strain X1EFGD (b), and at 120 h for strain X1D (c) after the start of cultivation. (B) Characterization of oligosaccharides P4 and P5. The culture medium of strain X1D from the experiment represented in panel A, row c, was incubated with or without the cells of strain BsrAXH expressing the extracellular arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH). After incubation, the samples were centrifuged, and the supernatants were analyzed by LC-ESI-MS. The lower spectrum was from the sample treated with (+) AXH, and the upper one was from the sample without (−) AXH. Compounds P4, P5, and P6 were oligosaccharides whose molecular weights corresponded to pentose-oligosaccharides composed of 4 to 6 pentose units. X2, xylobiose; X3, xylotriose; X4, xylotetraose.