FIG 1.
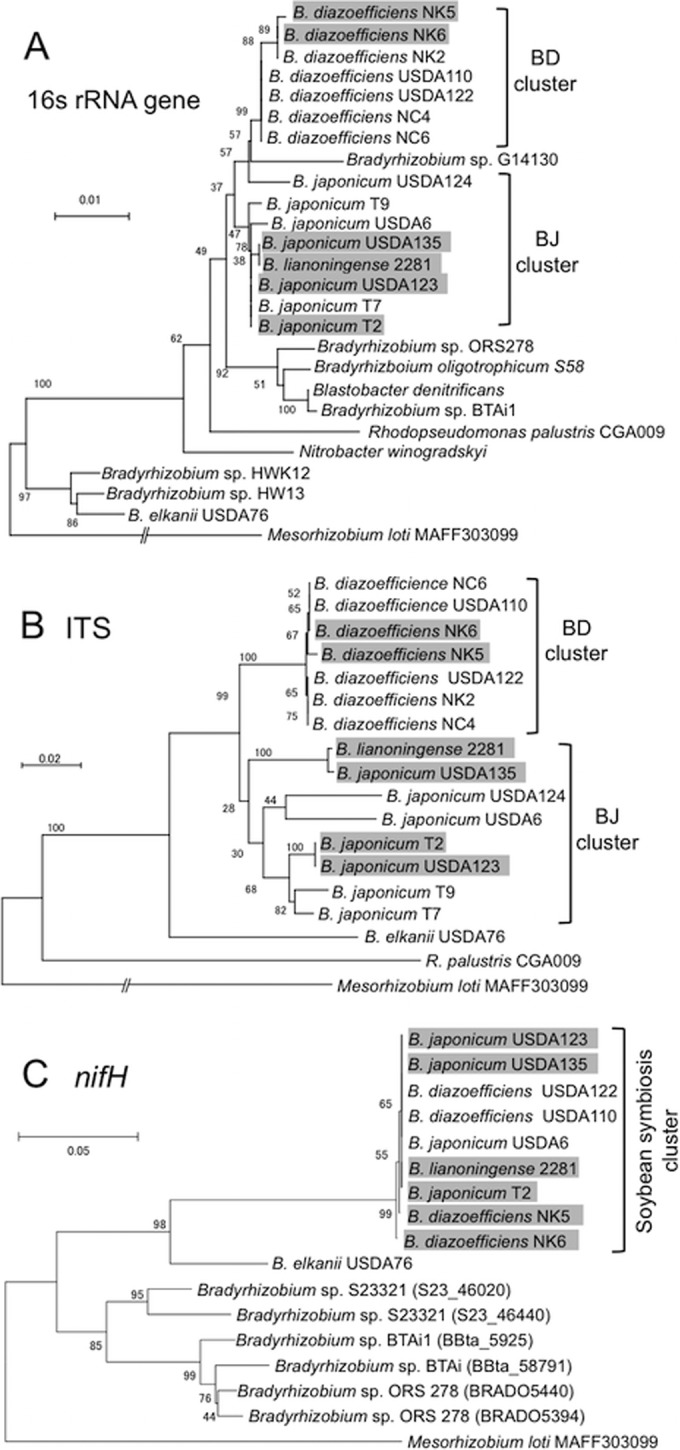
Phylogenetic relationships among HRS and non-HRS strains of soybean bradyrhizobia based on the sequences of 16S rRNA genes (A), internal transcribed spacers (ITS) (B), and nifH genes (C). HRS strains are shaded in gray. For all trees, Mesorhizobium loti MAFF303099 was used as an outgroup (1). Numbers at the nodes are percentages of 1,000 bootstrap replications supporting that partition. Bars show the number of base substitutions per nucleotide. Clusters BD in panels A and B include B. diazoefficiens strains; clusters BJ include B. japonicum and B. lianoningense strains. The soybean symbiosis cluster in panel C includes BD and BJ strains able to nodulate soybean and fix nitrogen. Reference strains of the Bradyrhizobiaceae and their sequences were described previously (6).
