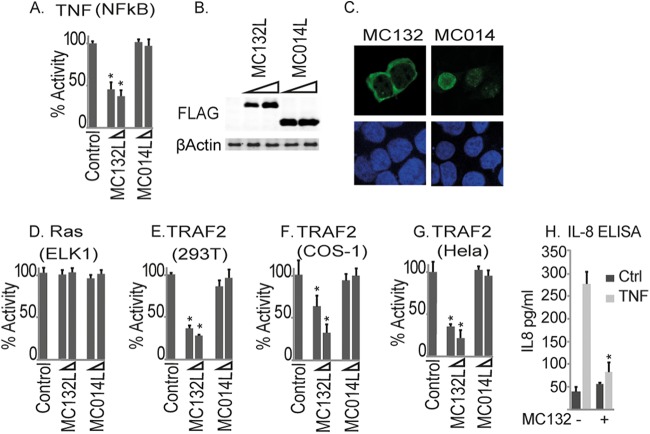
FIG 1.
Identification of MC132 as an inhibitor of TNF-α-stimulated NF-κB activation. (A) HEK293T cells were seeded at 2 × 105 cells per ml, transfected with 80 ng NF-κB reporter gene, 40 ng TK renilla reporter gene, and 25 or 50 ng (indicated by wedge) empty vector (control) or pCEP4 plasmids expressing the indicated MCV ORFs, stimulated with 50 ng/ml TNF-α for 6 h, and then harvested and assayed for NF-κB reporter gene activity. Data are percentages of the stimulation activity for control cells and are means ± standard deviations (SD) for triplicate samples from a representative experiment (n = 3). (B) Extracts from the samples used for panel A were probed for expression of Flag-tagged viral proteins. (C) Localization of MC132 and MC014 in HEK293T cells. Cells were transfected with 3 μg pCEP4-Flag vector containing the indicated MCV ORFs. Cells were fixed 24 h later and stained with DAPI (blue) or for MCV protein expression (green). Representative images are shown (n = 4). (D) Elk1 activation by Ras in cells transfected with empty vector (control) or pCEP4 plasmids expressing MCV ORFs was measured by a reporter gene assay. Data are percentages of the stimulation activity for control cells for a representative experiment performed in triplicate (n = 3). (E to G) The same as panel A, except that HEK293T (E), COS-1 (F), or HeLa (G) cells were transfected with 50 ng TRAF2-Flag instead of TNF-α stimulation. (H) Cells stably expressing pMEP4-MC132 were seeded at 2 × 105 cells per ml, cultured with (+) or without (−) 1 μM CdCl2 to induce MC132 expression, and then, 24 h later, stimulated with 50 ng/ml TNF-α for 24 h. IL-8 production was then assayed by ELISA. Data are means ± SD for triplicate samples from a representative experiment (n = 3). *, P < 0.001 compared to the control.