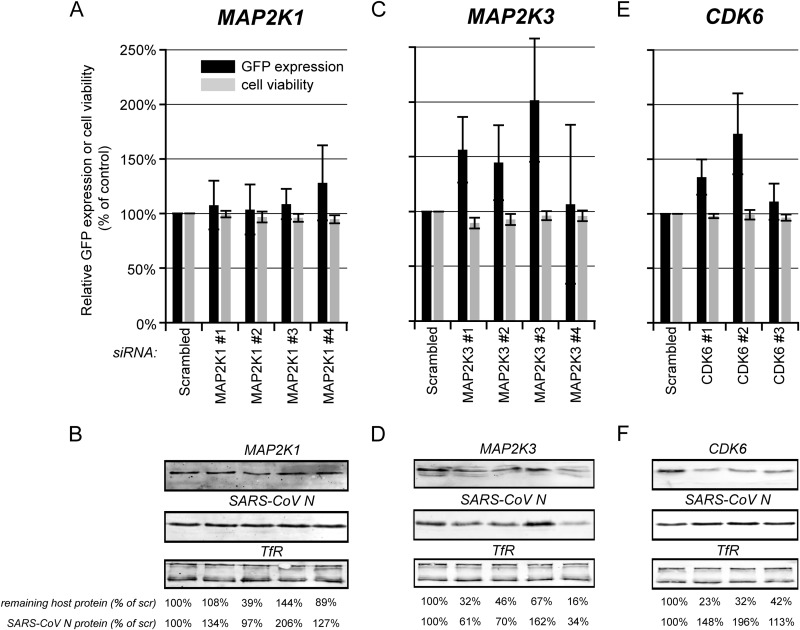
FIG 6.
Evaluation of the antiviral hits CDK6, MAP2K1, and MAP2K3. 293/ACE2 cells were transfected with four individual siRNAs targeting, MAP2K1 (A and B), or MAP2K3 (C and D) or three CDK6-specific siRNAs (E and F). A nontargeting scrambled siRNA was used as a control. At 48 h p.t. cells were infected with SARS-CoV-GFP at an MOI of 10 (A, C, and E) and fixed 24 h later, and GFP fluorescence (black bars) was quantified and normalized to the value measured in infected, scrambled siRNA-transfected cells (100%). The effect of siRNA transfection on cell viability was analyzed in parallel (gray bars), and values were normalized to those of scrambled siRNA-transfected control cells (100%). Each experiment was repeated at least three times (averages ± standard deviations [SD]). In parallel, siRNA-transfected cells were infected with wt SARS-CoV (MOI, 5), and at 8 h p.i., SARS-CoV N expression was monitored by Western blotting (B, D, and F). TfR was used as a loading control. Knockdown levels of the host proteins were analyzed by Western blotting (B, D, and F). The amount of SARS-CoV N protein and remaining quantity of host protein compared to that of scrambled siRNA-transfected cells (100%) is shown below each lane. All experiments were repeated at least twice.