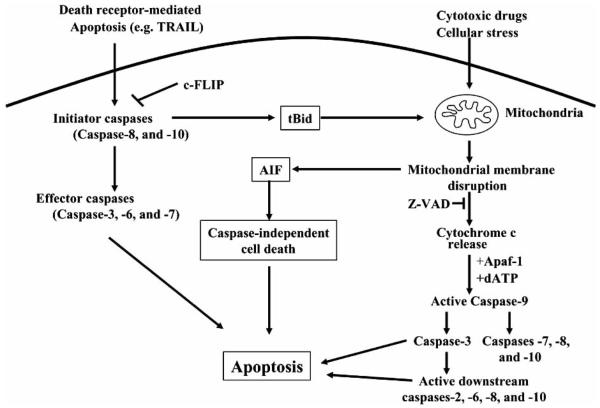
Fig. (1). Mitochondrial death pathway.
The mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis is usually caused by disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), release of cytochrome c, activation of caspase-9, and subsequent activation of downstream caspases-2, -3, -6, -7, -8 and -10, which eventually leads to apopto sis. On the other hand, caspase-dependent apoptosis induced by death receptor ligation (e.g., Fas ligand/Fas or TNF-α/TNF- α receptor) can function independently of the mitochondria by caspase-8 activation, which directly activates caspase-3, -6 and -7, or by causing proteolytic cleavage of the pro-apoptotic protein Bid to a truncated form (tBid), which in turn is inserted in the mitochondrial membrane and induces release of cytochrome c. Release of the apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) from mitochondria causes caspase-independent apoptosis.