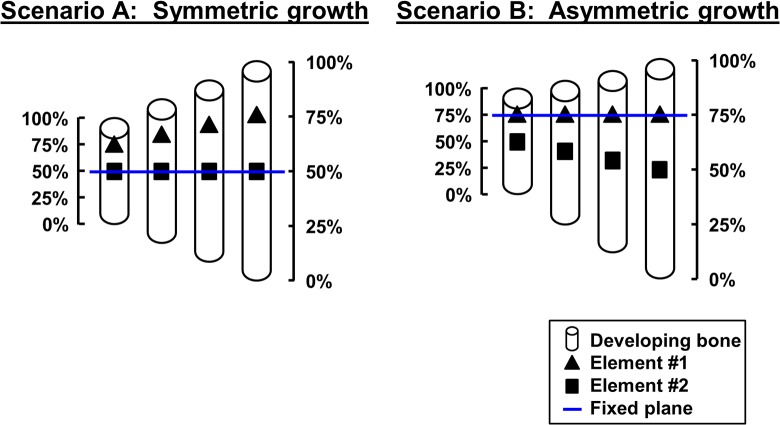
Fig 7. The fixed plane model for isometric scaling of long bones.
Illustration of fixed planes formed at the transverse plane where the ratio between the distances from the distal and the proximal ends of the bone is equal to the ratio between the distal and the proximal growth rates. (A) When growth is symmetric, the relative position of an element located at 50% length (rectangle) is maintained, whereas an element located at 75% length (triangle) drifts proximally to maintain its relative position. (B) When distal growth rate is three times higher than proximal growth rate, the location of the FP is at the 75% length. As a result, the relative position of the triangle element is maintained, whereas the rectangle element drifts distally to maintain its relative position.