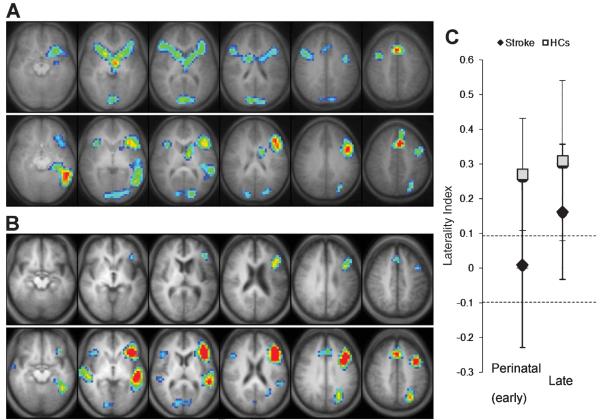
Fig. 2.
Statistical activation maps (corrected p < 0.05) for the verb generation task performed during fMRI in each of the groups (A, B) and corresponding global laterality index (LI) values (C). Activation clusters are overlaid onto axial slices of an averaged anatomical image of all subjects in each group, spanning z = −10 (left) to z = +40 (right). All images are shown in radiological convention (left in image is right in the brain). (A) Patients who suffered perinatal stroke (top row) show more symmetrical activation than their sex-/age-matched healthy controls (HCs; bottom row). (B) Patients who suffered a late stroke (top row) show less activation overall but similar left-lateralized pattern compared to their HCs (bottom row). (C) Global LI (mean ± SD) used to determine language laterality (i.e., dashed lines with LI > 0.1 as leftward, LI <− 0.1 as rightward, and −0.1 ≤ LI ≤ 0.1 as symmetric) is significantly higher in both HCs compared to their respective stroke groups.