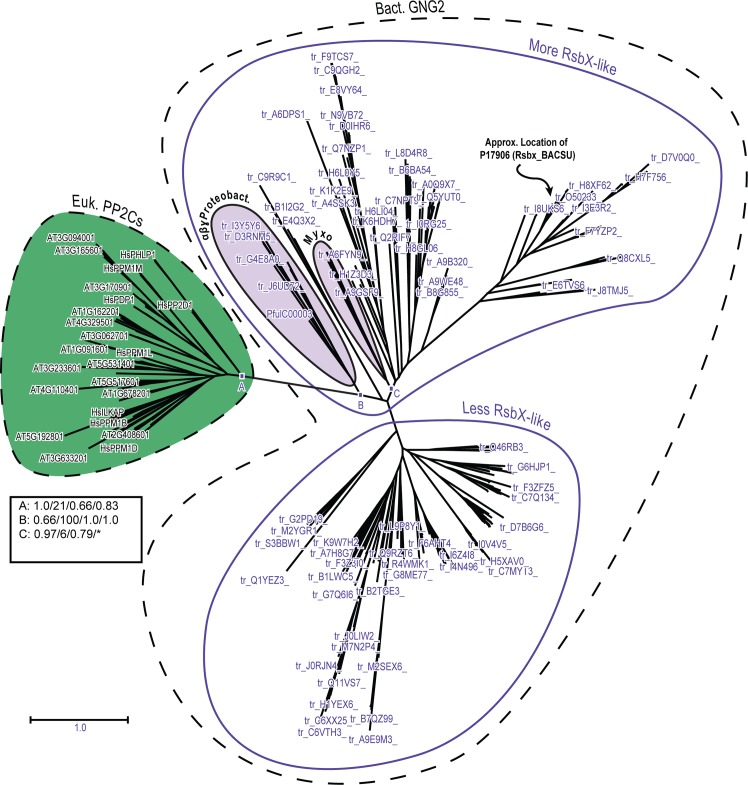
Fig 5. Phylogenetic radial tree depicting interrelationships between eukaryotic PP2C sequences and bacterial Group II PP2C sequences.
The eukaryotic PP2C set consists of the combined sequences (excluding PP2C7s) from Arabidopsis and human (96 sequences total—HsTAB1 excluded). The bacterial Group II sequences are of the “GN” type, including the “More RsbX-Like” and “Less RsbX-Like” assemblages (328 sequences total) (see text for explanation of sequence varieties). Inference of unrooted phylogenetic trees was performed as outlined in “Materials and Methods.” The most crucial nodes are labeled. Node support values with the four inference methods (PhyML [aBayes], RAxML [RBS], MrBayes [PP], and PhyloBayes_MPI [PP]) are tabulated in the Figure, separated by slashes (“/”). Support values for all trees are summarized in Table N in S1 File. The cluster of sequences from αβγ-Proteobacteria is indicated. “Myxo” designates sequences from the Myxococcales (δ-Proteobacteria). The approximate location in the tree of the reference sequence BsP17906 (RsbX_BACSU) is indicated. This tree is based on the amino acid sequence alignment presented in Fig A in S2 File, Panel 3. * = Myxococcales unresolved from other sequences in this tree.