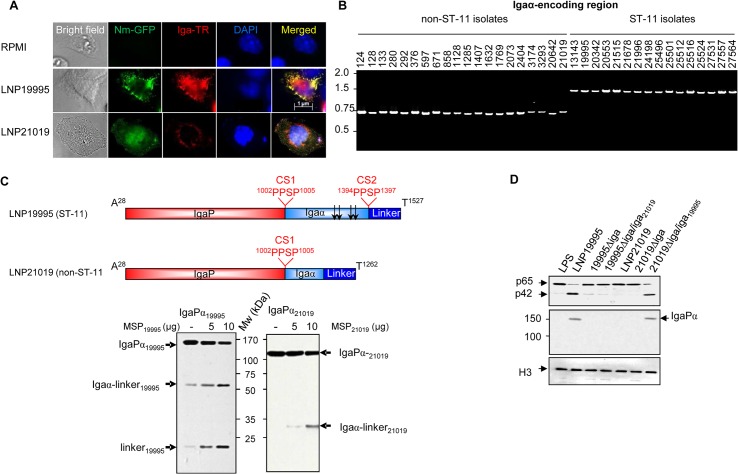
Fig 6. Non-ST-11 isolates release α-peptide-lacking IgA protease.
(A) Subcellular localisation of IgA protease in infected cells. Hec-1B cells were infected with GFP-expressing LNP19995 or LNP21019 (green) or left uninfected. After 12 h of infection, cells were fixed with 4% PFA, permeabilised and stained with anti-IgaP polyclonal serum and Texas Red (TR)-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Fluorescence was analyzed using immunofluorescence microscopy. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Analysis of ST-11 and non-ST-11 isolates by PCR using primers specific to α-peptide sub-domain. PCR products were amplified from genomic DNA of strains indicated above the gel, using the couple of primers alphaFwNhe / alphaRevSma. PCR products were separated by electrophoresis in 1% agarose gels and stained with ethidium bromide. PCR amplification generated amplicons of ~ 1500 bp in all ST-11 isolates, while amplicon sizes ranged between 687 and 770 bp in non-ST-11 isolates. Molecular sizes (kb) are indicated in the left side. (C) Upper panel. Non scaled schematic representation of the passenger subdomains of meningococcal IgA protease from isolates LNP19995 (ST-11) and LNP21019 (non-ST-11). The positions of autocatalytic processing sites and their sequences (PPSP) are indicated. Arrows indicate positions of NLSs in α-peptide of the ST-11 isolate. Lower panel. Five hundred nanograms of the C-terminal His6-tagged passenger domain of the strains LNP19995 (IgaPα19995) or LNP21019 (IgaPα21019) were mixed with 5 or 10 μg of MSPs. After 3 h, the reaction mixtures were analyzed with immunoblot using anti-His tag mAb. The different cleavage products are indicated by arrows. Mw indicates the molecular weight. (D) IgA protease of ST-11 isolates restores the capacity of non-ST-11 isolates in cleaving nuclear p65. Each of the 19995Δiga and 21019Δiga were complemented with the heterologous iga allele of the WT strain LNP21019 and LNP19995, respectively. Hec-1-B cells were infected for 12 h with the parental WT strains, the isogenic iga knock-out mutant strains or the heterologous complemented strains. Nuclear fractions prepared from infected cells, were resolved by SDS-PAGE and were probed with anti-p65 mAb (N-terminal specific) or polyclonal serum anti-IgaP. LPS-treated cells were used as positive control for nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Immunoblot with anti histone H3 was used as loading control.