Fig. 2.
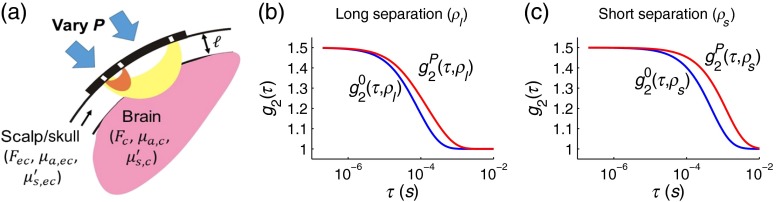
(a) Two-layer tissue model of the head, which is composed of a semi-infinite bottom layer (i.e., corresponding to the cortical regions of the brain) with a distinct blood flow index, absorption coefficient, and reduced scattering coefficient of , , and , respectively, and a superficial top layer (i.e., corresponding to extracerebral scalp and skull tissue) with thickness , and distinct tissue properties denoted by , , and . The head is probed with a long source-detector separation, (yellow shading), and a short source-detector separation, (red shading), and the probe pressure against the head is varied. Increasing the probe pressure from (blue curves) to (red curves) induces a change in the diffuse correlation spectroscopy (DCS) signal [] at both the long separation (b) and the short separation (c). These signal changes arise entirely from pressure-induced changes in extracerebral flow.28
