Figure 1.
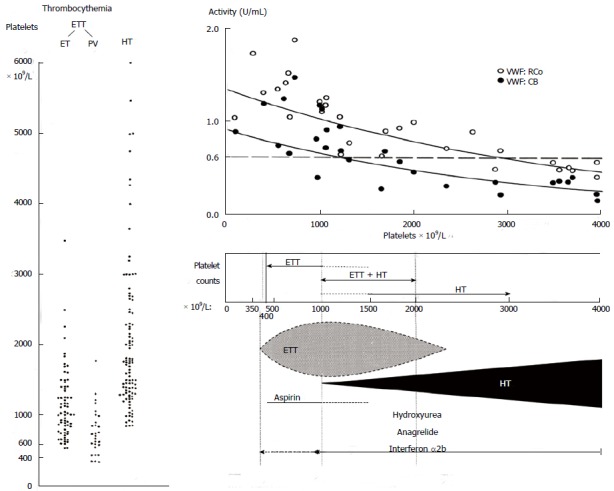
Platelet counts in 100 case histories of hemorrhagic thrombocythemia and 99 cases of erythromelalgic thrombotic thrombocythemia subdivided in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera (left)[1,2]. The relationship between platelet-mediated microvascular thrombosis in ETT at platelet counts between 350 to 1000 × 109/L in ETT and mucocutaneous bleedings at platelet counts between about 1000 to above 2000 x 109/L in HT patients (Table 3)[1-7]. The relationship of increasing platelet counts and decreasing von Willebrand factor (VWF) levels, VWF:ristocetine cofactor activity (VWF:RCo), and VWF collagen binding activity (VWF:CB) as the cause of an acquired Von Willebrand Disease (AVWD) type 2A due to proteolysis of large VWF nultimers in patients with paradoxical occurrence of ETT and HT and in patients with HT[8]. HT: Hemorrhagic thrombocythemia; ETT: Erythromelalgic thrombotic thrombocythemia; ET: Essential thrombocythemia; PV: Polycythemia vera.
