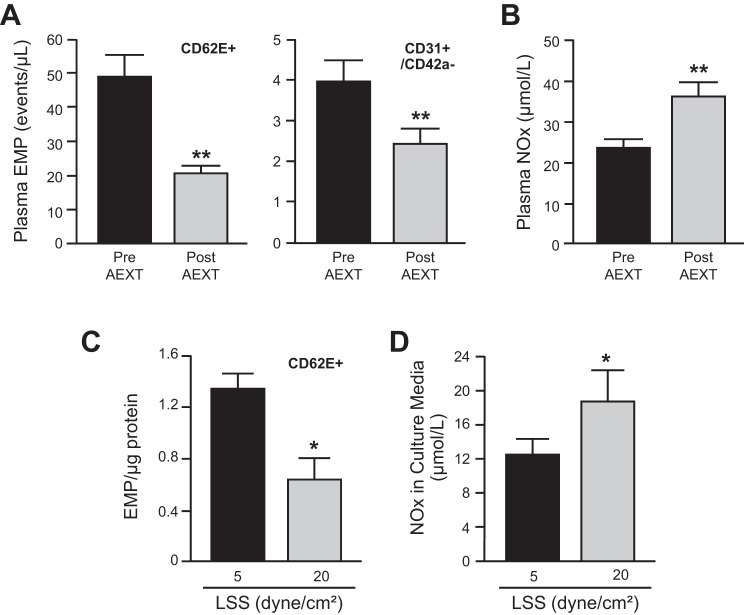
Fig. 1.
Effects of aerobic exercise training (AEXT) and shear stress on endothelial cell microparticle and nitric oxide production. A and B: plasma CD62+ endothelial cell microparticle (EMP), CD31+/CD42a− EMP, and nitric oxide (NOx) levels from human subjects at before (pre) and after (post) 6-mo AEXT (n = 21). C and D: 7 separate human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) cell lines from 7 different donors were exposed to either low (5 dyne/cm2) or high (20 dyne/cm2) laminar shear stress (LSS) for 24 h. Accumulated CD62+EMP and NOx were measured from the cell culture media. Each column represents means ± SE. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.