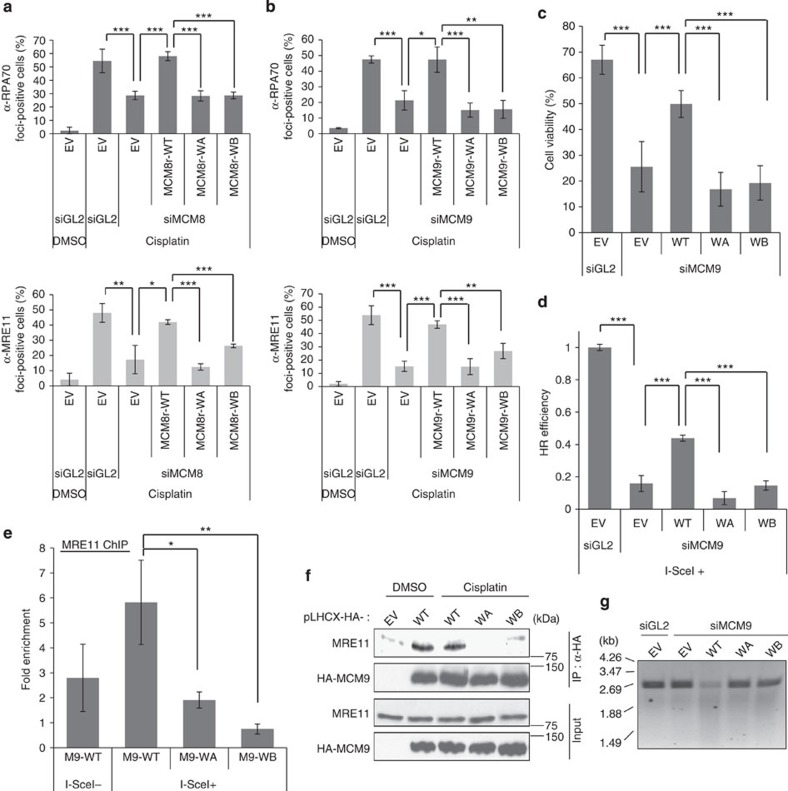
Figure 4. ATPase motif of MCM9 is essential for HR repair and the interaction with MRE11 protein.
(a,b) Mutation on ATPase motif of MCM8-9 decreases RPA (top) or MRE11 (bottom) foci formation. U2OS cells supported by Walker A- (WA) or Walker B (WB) mutants of MCM8 (a) or MCM9 (b) were treated with cisplatin after knockdown of the endogenous protein, and foci-positive cells were counted as described previously. ***P<0.005, **P<0.01, *P<0.05; Student's t-test. (c) WA- or WB mutant of MCM9 cannot restore resistance to cisplatin after knockdown of endogenous MCM9. Cell viability was measured by colony count at day 5 after cisplatin treatment . ***P<0.005; Student's t-test. (d) WA- or WB mutant MCM9 cannot rescue HR. HR assays were performed in HeLa DR13-9 cells having stable expression of siRNA-resistant MCM9. HR efficiency was measured by normalizing the percentage of GFP-positive cells of each sample to that of the siGL2-treated cells. ***P<0.005; Student's t-test. (e) WA- or WB mutant MCM9 cannot recruit MRE11 to I-SceI cut site. ChIP was done using HeLa DR13-9 cells having stable expression of siRNA-resistant MCM9 after knockdown of endogenous MCM9. Signal at cut site expressed relative to -2 kb site. **P<0.01, *P<0.05; Student's t-test. (f) WA- or WB mutant MCM9 does not co-immunoprecipitate MRE11 from HEK293T cells transfected by the indicated plasmids expressing MCM9. (g) Decrease in nuclease associated with WA- or WB mutant MCM9. DNA products visualized after in vitro nuclease assay for 90 min with epitope-tagged MCM9 immunoprecipitated (IP) from cells transfected with indicated plasmids and siRNAs as described in Methods section. Cells were treated with 40 μM cisplatin for 4 h before harvest. All error bars represent s.d. of the mean from triplicates. EV, empty vector; WT, wild type.