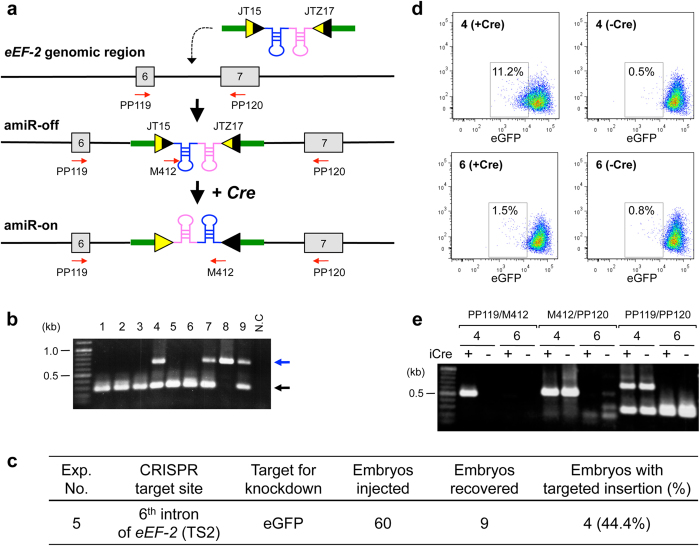
Figure 4. Targeted insertion of ssDNA encoding Cre-activatable anti-eGFP amiRNA by CRISPR/Cas9 system (Exp. 5).
(a) Schematics of targeted integration of reverse orientated ‘amiR-eGFP123/419’ and mutant loxP sites (JT15 and JTZ17) into the intron 6 of eEF-2 gene and subsequent Cre-loxP recombination to switch the amiRNA cassette to the right orientation. Functional amiRNAs do not get produced from the targeted ‘amiRNA-off’ allele because of the opposite orientation of amiRNA with respect to the eEF-2 gene. After Cre recombination, the allele gets converted to ‘amiRNA-on’ that produces functional amiRNA. Red arrows indicate the primers (PP119, PP120 and M412) used for genotyping. (b) Genotyping of fetuses by PCR using primer set (PP119/PP120). Expected fragment sizes: wild-type = 301-bp (black arrow), targeted insertion = 705-bp (blue arrow). (c) Targeted insertion efficiency. (d) Dotplot of embryonic feeder cells, derived from Exp. 5 samples #4 (upper) and #6 (lower), nine days after transfection with (left) or without (right) the iCre plasmid. The cells showing weak eGFP fluorescence are partitioned within the box in each plot. (e) Genotyping of embryonic feeder cells used in the experiment (d) by PCR with primer sets shown in (a).