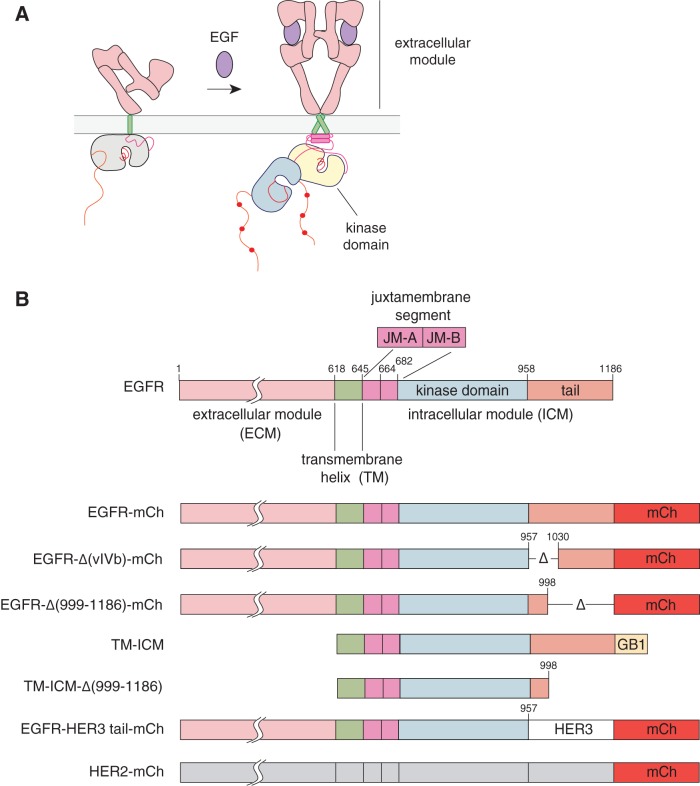
FIG 1.
Model for activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and constructs used in this study. (A) Ligand binding to the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor induces a conformational change that results in receptor-mediated dimerization and activation. Activation of the intracellular kinase domains is promoted by the formation of an asymmetric dimer, in which one kinase domain (the activator [yellow]) activates the other kinase domain (the receiver [blue]). (B) Domain architecture of human EGFR with domain boundaries highlighted. The domain composition of the EGFR family constructs used in this study is also presented, including EGFR deletion constructs, the EGFR-HER3 tail chimera, and HER2 (Δ, deletion; mCh, mCherry fluorescent protein fusion).