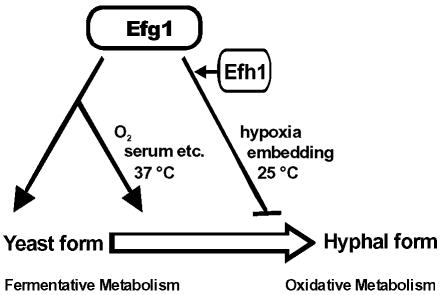
Figure 10.
Model of APSES protein functions in C. albicans. Efg1p favors the yeast growth form and a fermentative mode of metabolism. It also is required for the transition from the yeast to the hyphal growth form, which is initiated by inducers including serum. In embedded and hypoxic conditions, at lower temperatures, Efg1p represses rather than induces hypha formation. Efg1p could act directly, as a direct transcriptional activator, or indirectly, by repressing yet undefined repressors of morphogenesis and metabolism (as suggested by Efg1p-repressor function in one-hybrid experiments). Efh1p enhances the activation and repression functions of Efg1p in metabolism and morphogenesis, presumably by activation of EFG1 expression; Efh1p may also have yet unknown Efg1p-independent functions.