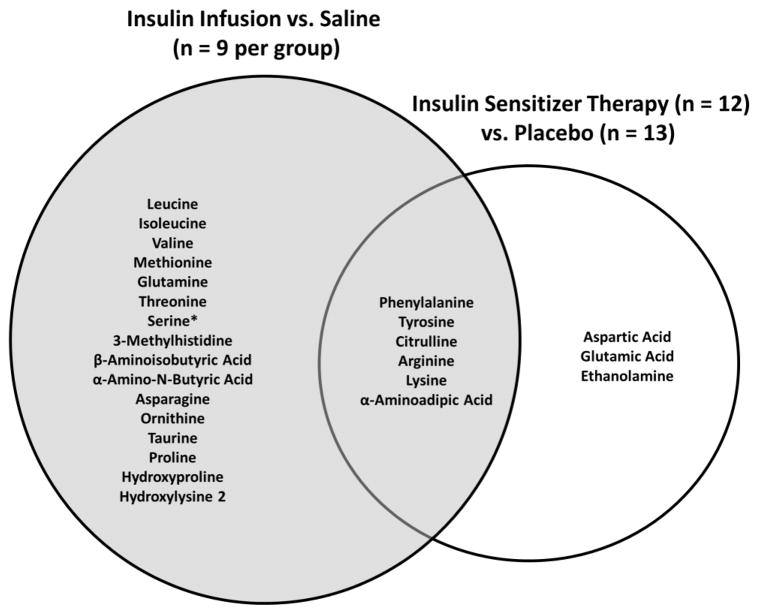
Fig. 2.
Venn diagram for plasma amino acid and amino acid metabolites that were reduced in response to an acute or chronic increase in insulin action. Compared to saline, 22 amino acids and amino acid metabolites were reduced in response to an acute infusion of insulin in healthy young adults (n = 9 per group) (grey circle). Compared to placebo, nine amino acids and amino acid metabolites were reduced in response to three months of insulin sensitizer therapy in overweight/obese (BMI~30 kg/m2) adults with impaired fasting glucose or untreated diabetes (n = 13, placebo; n = 12 insulin sensitizer) (white circle). Three functional pairs of amino acids and amino acid metabolites (phenylalanine/tyrosine, lysine/α-aminoadipic acid, and arginine/citrulline) were reduced in response to both the acute infusion of insulin as well as three months of insulin sensitizer therapy. Finally, serine concentrations were reduced in response to the acute infusion of insulin, while it was increased in response to three months of insulin sensitizer therapy.