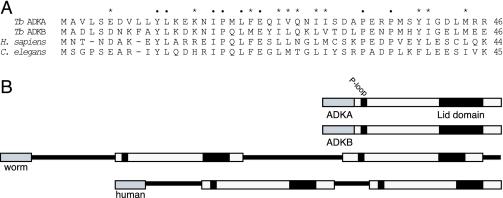
Figure 6.
Identification of unusual adenylate kinases in C. elegans and Homo sapiens. (A) Sequence alignment of the first 46 amino acids of TbADKA and TbADKB with two sequences that were identified when these N-terminal regions were used in blast analysis of the genome databases available at National Center for Biotechnology Information. Positions of identity in all four sequences are highlighted using black dots; asterisks indicate positions where functional similarity is conserved. (B) When the two novel sequences were examined more closely (accession nos. CAA15625 [C. elegans] and NP_777283 [H. sapiens]) both proteins were found to be tandem adenylate kinases in which both putative catalytic domains were downstream of the conserved N-terminal region shown in A.