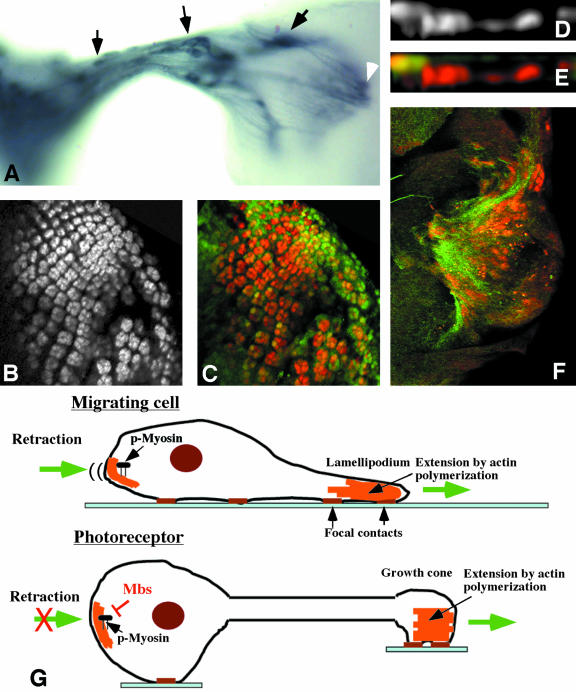
Figure 6.
Mbs mutant photoreceptors move toward their axon terminals. (A) Third instar eye disc-brain complex containing unmarked MbsT541 clones, stained with anti-Chaoptin to label all photoreceptor cell membranes. Mislocalized cell bodies are visible within the optic stalk and the lamina (arrows). The latter cells project into the medulla (white arrowhead). (B-F) Eye discs containing MbsT666 clones generated in a disco1 background. Photoreceptors are stained with anti-Elav (B and D, red in C, E, and F), and wild-type tissue is marked with GFP in green (C and E). Photoreceptors still move basally in disco mutants. (F) Basal focal plane with axons stained with anti-Chaoptin (green). Mislocalized nuclei are present close to a concentration of axons. (G) Comparison of cell migration to neuronal axon extension. Actin polymerization is important to extend the leading edge of a migrating cell and the growth cone of a neuron. During cell migration, phosphorylated myosin retracts the rear of the cell. Mbs may prevent a similar retraction of neuronal cell bodies.