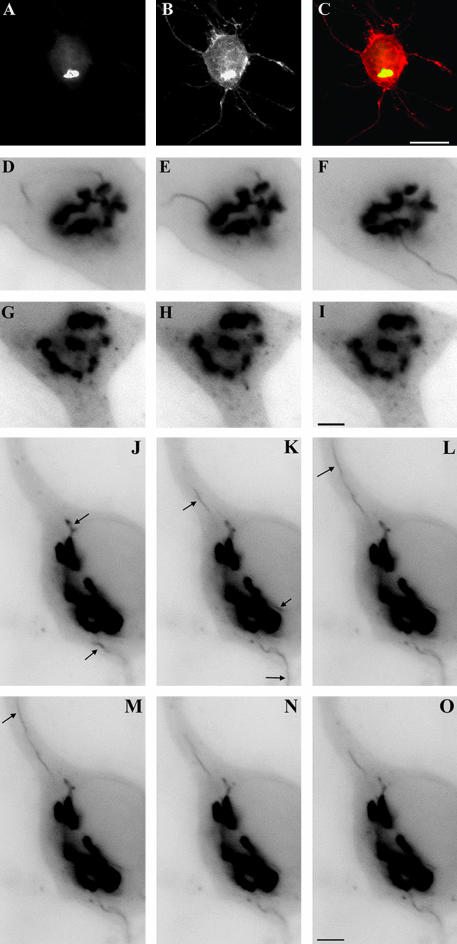
Figure 3.
LIMK1 regulation of Golgi dynamics. (A-C) Fluorescence micrographs showing the distribution of galactosyl-transferase T2-EYFP fusion protein (A) and HA-tagged wt-LIMK1 (B) in a cultured hippocampal pyramidal neuron; the image in C shows the red-green overlay of the images shown in A and B. Note the strong colocalization of both proteins at the Golgi apparatus. (D-F) Sequence of fluorescence images showing the dynamics of the Golgi apparatus from a neuron transfected with galactosyl-transferaseT2-EYFP; the EYFP signal is shown in black. Note the presence of tubulo-vesicular processes emerging from the Golgi stacks. (G-I) A similar sequence to that described previously, but from a cell cotransfected with galactosyl-transferase T2-EYFP and HA-tagged wt-LIMK1. Note the absence of tubulo-vesicular processes emerging from the Golgi stacks and the presence of small vesicles within the cell cytoplasm. (J-O) A sequence of fluorescence images showing the dynamics of the Golgi apparatus from a neuron cotransfected with galactosyl-transferase T2-EYFP and HA-tagged LIMK1-kd. Note the presence of several tubulo-vesicular processes (arrows) emerging from the Golgi stacks that persist for longer periods of time than the ones observed in cells transfected with galactosyl-transferaseT2-EYFP alone; parts of the labeled tubules are out of the plane of focus. For all these experiments cells were visualized 12 h after transfection and each image was taken at 30-s intervals. Bars, 10 μm (A-C) and 2.5 μm (D-O).