Fig. 2. Two possible ways for large bound errors to occur during the design search.
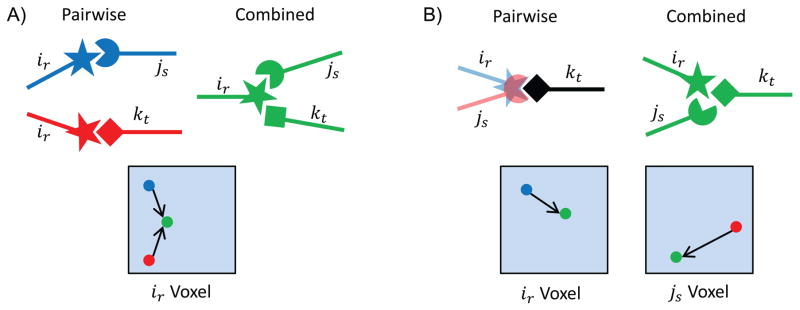
A) When ir is pairwise minimized with two different rotamers, js and kt, the optimal position of ir is different for the two pairwise interactions. When all three rotamers are minimized simultaneously, ir cannot be in two places at once, so the globally optimal positioning of the rotamers is suboptimal with respect to the pairwise interactions. Therefore, the global minimum for all three rotamers is higher than the optimal pairwise minima. The shaded box represents the continuous voxel for continuous rotamer ir. The colored dots show schematically the movement of the ir rotamer within its voxel from its pairwise optimal positioning (with js, blue; with kt, red) to its globally optimal positioning (green). B) Two rotamers, ir and js, may minimize to the same real space position, but when minimized simultaneously protein sterics does not allow the rotamers to occupy the same Cartesian coordinates. As in A), the global minimum for all three rotamers is suboptimal relative to the pairwise bounds, resulting in a global minimum that is higher than the pairwise minima. The shaded boxes represent the continuous voxels for rotamers ir and js. The colored dots show schematically the movement of the ir and js rotamers within their voxel from their pairwise optimal positioning (blue and red) to their globally optimal positioning (green).
