Figure 1.
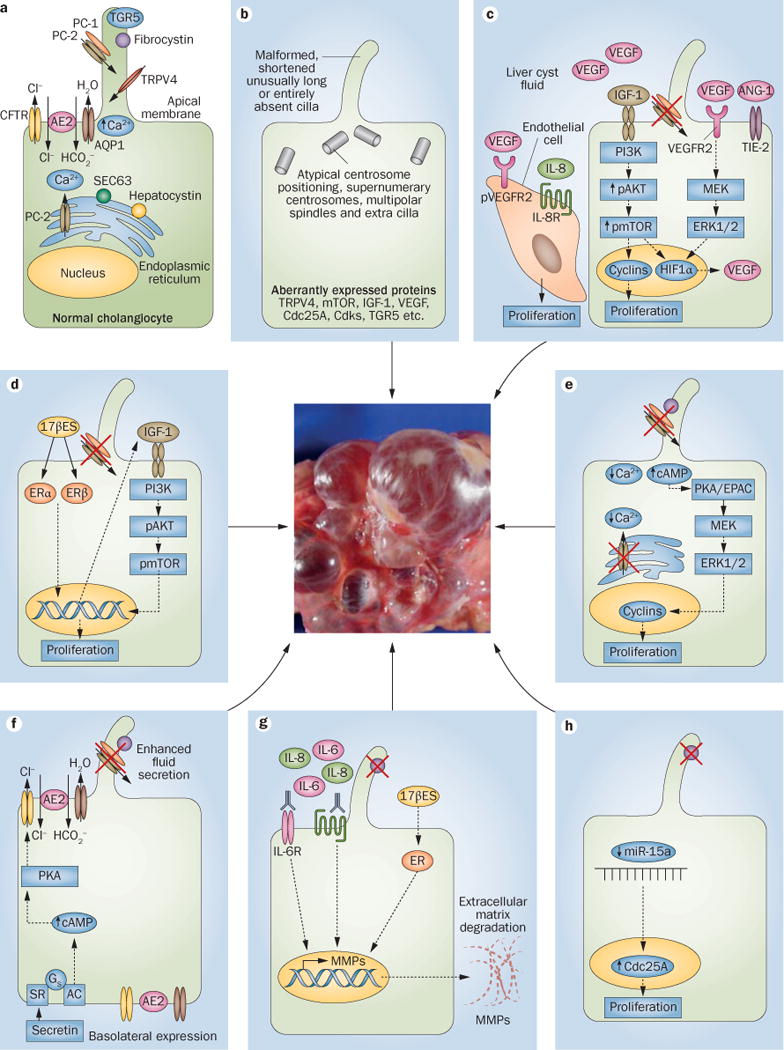
Cellular alterations and molecular mechanisms involved in hepatic cystogenesis. a | The normal structure of both a cholangiocyte and a primary cilium. b | The primary cilium and gene expression levels of key intracellular mediators can be altered in polycystic liver diseases. c | Different growth factors and cytokines stimulate the proliferation of cystic cholangiocytes and endothelial cells in an autocrine and/or paracrine fashion. Moreover, d | oestrogens and e | changes in intracellular calcium and cAMP levels might also induce the proliferation of cystic cholangiocytes. Hepatic cystogenesis is associated with f | alterations in fluid secretion and g | extracellular matrix remodelling. h | Global downregulation of microRNAs occurs in cystic cholangiocytes, which facilitates the proliferation of cystic cholangiocytes. The relative involvement of each pathway in different forms of hepatic cystogenesis has been highlighted in the main body text. The central image is of human liver tissue with cysts. Abbreviations: 17βES, 17β oestradiol; AC, adenylate cyclase; AE2, anion exchanger 2; ANG-1, angiopoetin-1; AQP1, aquaporin 1; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; Cdc25A, cell division cycle 25A; Cdks, cyclin dependent kinase; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; EPAC, rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 3; ER, oestrogen receptor; ERα, oestrogen receptor α; ERβ, oestrogen receptor β; ERK1/2, extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2; Gs, Gs protein; HIF1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1α; IGF1, insulin-like growth factor 1; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1; miR-15a, microRNA 15a; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; pAKT, phosphorylated v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1; PC-1, polycystin-1; PC-2, polycystin-2; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase; PKA, protein kinase A; pmTOR, phosphorylated mTOR; pVEGFR2, phosphorylated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; SEC63, SEC63 homolog; SR, serotonin receptor; TGR5, g-protein coupled bile acid receptor-1; TIE-2, TEK tyrosine kinase; TRPV4, transient receptor potential cation subfamily V member 4; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
