Figure 4.
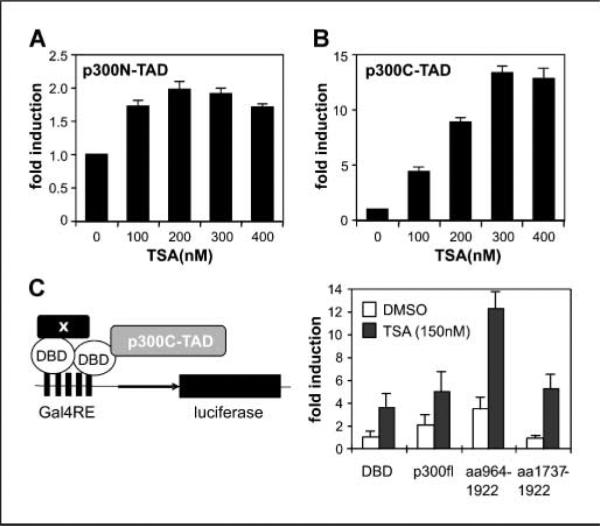
The p300C-TAD is affected by acetylation. A, effects of TSA on the transactivation potential of p300aa1-596. Gal4-p300N-TAD (amino acids 1–596) was cotransfected (3 μg) with the luciferase reporter (3 μg) and pCMV-LacZ (0.5 μg). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were split evenly into 15 wells of 12-well culture plates and treated with various doses of TSA in triplicate. RLUs were normalized to β-galactosidase activity and induction factors are given. B, effects of TSA on p300C-TAD. Experiments were done as in (A), except that Gal4-p300C-TAD (amino acids 1,737–2,414) was used in cotransfection. C, synergetic effects of p300HAT and TSA. The assay system is outlined on the left. Plasmid expressing Gal4-p300C-TAD (2 μg) was cotransfected with indicated plasmid (2 μg) in reporter assays. RLUs were normalized first to β-galactosidase activity and calculated into fold of enhancement for comparison. Data showed that corecruitment of p300 full-length (fl) or p300HAT domain to the Gal4 promoter enhanced the transactivation potential (open columns) and increased the sensitivity of Gal4-p300C-TAD to TSA (solid columns, 150 nmol/L). Bars, SD.
