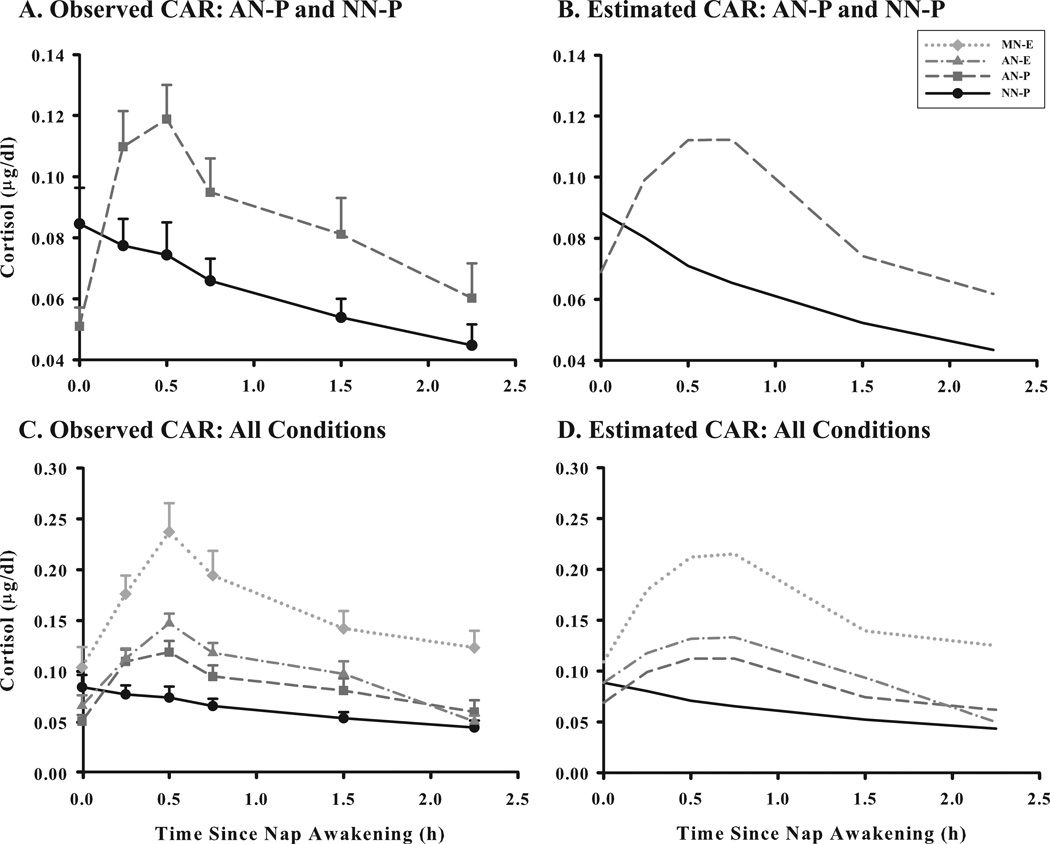
Figure 2.
Average cortisol awakening response (CAR) profiles (n=28) for four napping conditions: i) morning nap – experimenter collected samples (MN-E); ii) afternoon nap – experimenter collected samples (AN-E); iii) afternoon nap – parent collected samples (AN-P); and iv) no-nap – parent collected samples (NN-P; sample times matched to AN-P). Salivary cortisol (µg/dl) samples were obtained at 0, 15, 30, 45, 90, and 135 minutes after nap wake time (verified objectively with actigraphy). Profiles for observed (A) and estimated (B) values of the CAR for AN-P and NN-P conditions and observed (C) and estimated (D) values for all CAR conditions using 3 models in HLM 6. Error bars represent SEM.