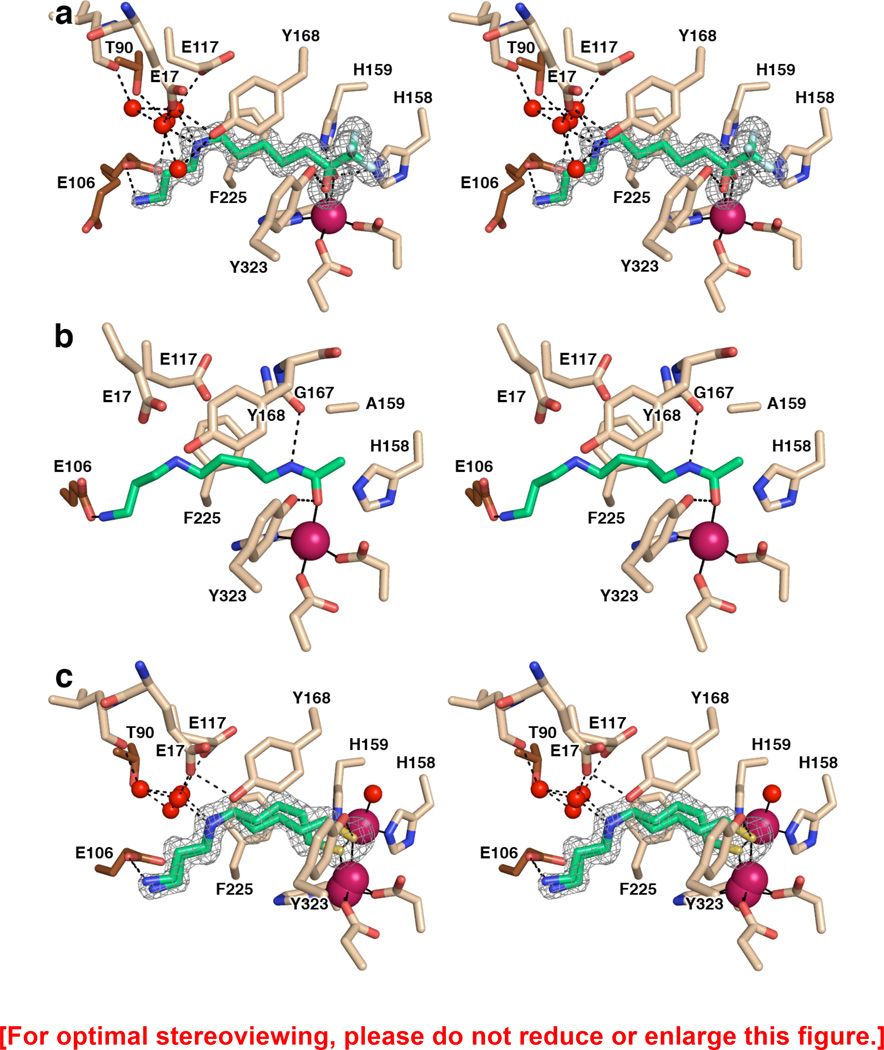
Figure 2.
(a) Simulated annealing omit map showing trifluoromethylketone 1 bound as a gem-diol in the active site of APAH (monomer B, contoured at 3.5σ). Atomic color codes are as follows: C = wheat (protein, monomer B), brown (monomer A), or green (inhibitor), N = blue, O = red, F = light cyan, Zn2+ = magenta sphere. Water molecules are represented as red spheres. Metal coordination and selected hydrogen bond interactions are shown as solid black or dashed black lines, respectively. (b) Stereoview of the N8-acetylspermidine substrate bound in the active site of the inactive mutant APAH H159A (PDB accession code 3Q9C, monomer A). Atomic color codes are identical to those in (a); C atoms in brown correspond to adjacent monomer I of the APAH dimer. We note that in monomer J only of this structure, the secondary amine of N8-acetylspermidine donates a hydrogen bond to E117. Additionally, a water molecule makes a bridging interaction in some monomers between Y19 and the terminal amino group of the substrate. (c) Simulated annealing omit map of thiol 2 bound in the active site of APAH (monomer A, contoured at 3.0σ). Atomic color codes are identical as in (a), with S = gold.