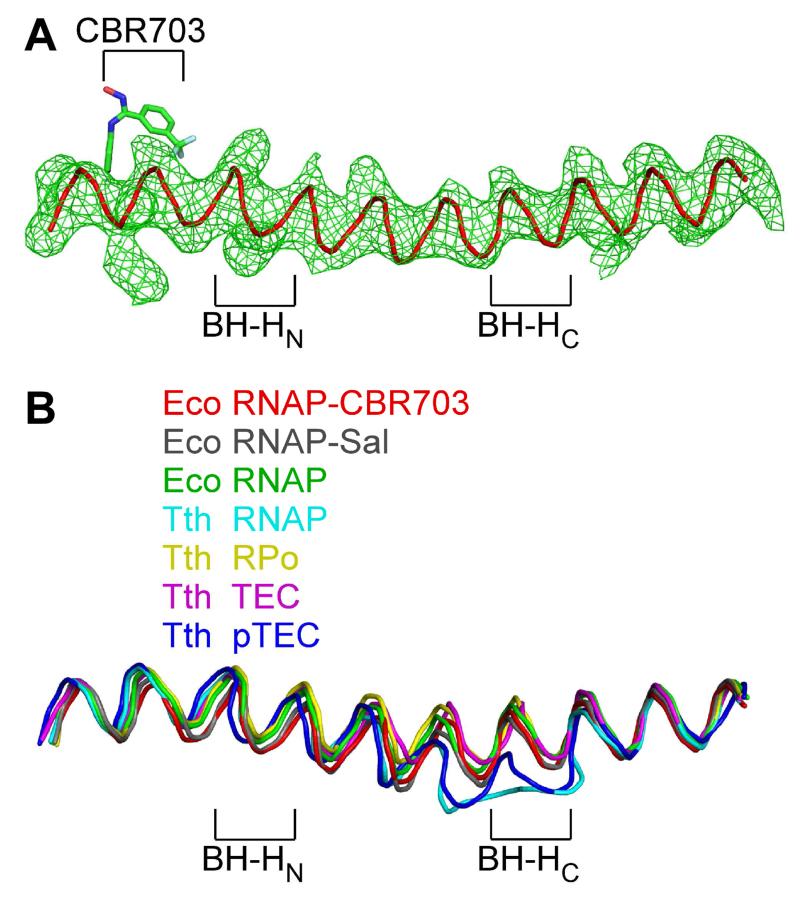
Figure 7. Relationship between the binding site and resistance determinant of CBR703 and the RNAP active center: CBR inhibitors interact with a straight, unbent state of the RNAP bridge helix.
(A) Electron density and model for bridge helix in crystal structure of RNAP-CBR703. Green mesh: mFo-DFc omit map for bridge helix (contoured at 2.5σ). Red ribbon: bridge-helix backbone. Green, red, blue, and cyan: CBR703 carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine atoms. BH-HN: bridge-helix N-terminal hinge. BH-HC: bridge-helix C-terminal hinge.
(B) Superimposition of bridge helices of E. coli RNAP-CBR703 (red; unbent BH-HN and BH-HC), RNAP-Sal (black; PDB: 4MEX), E. coli RNAP (green; PDB: 4MEY), T. thermophilus RNAP (cyan; PDB: 1IW7), T. thermophilus RPo (yellow; PDB: 4G7H), T. thermophilus transcription elongation complex (pink; PDB: 2O5J), and paused T. thermophilus transcription elongation complex (violet; PDB: 4GZY).