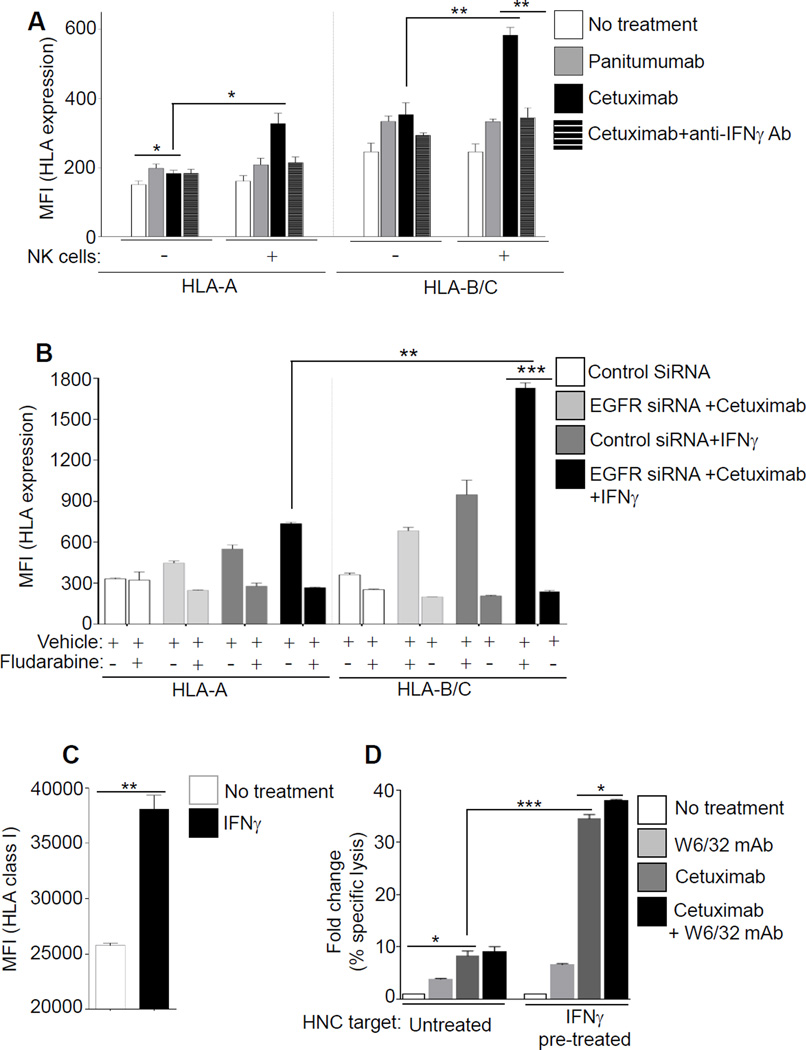
Figure 4. Cetuximab-activated NK cells and IFNγ increase expression of HLA class I APM pathway.
(A) JHU-029 HNC cells were cultured alone, or JHU-029 plus NK cells in co-culture (1:1 ratio) were left untreated or were treated for 48h with panitumumab (IgG2, 10 µg/ml), cetuximab (IgG1, 10 µg/ml). Levels of HLA-A (left panel) or HLA-B/C (right panel) were determined by FACS. In parallel, polyclonal anti-IFNγ Ab (10 µg/ml) was added at indicated conditions to determine the effect of IFNγ released from cetuximab-activated NK cells. (B) HNC cells were pre-treated with fludarabine (20 µM), and after EGFR siRNA or cetuximab treatment (48h, 10 µg/ml) levels of surface HLA-A, HLA-B/C were determined by FACS. (C) JHU-029 HNC cells were cultured alone, or were treated with IFNγ (10 U/ml, 36h) and enhanced levels of HLA class I (mAb W6/32) was verified with FCAS. (D) NK cell cytotoxicity (4h 51Cr release assay, 40:1 E/T ratio) against untreated or IFNγ pre-treated HNC targets (C), were independently evaluated in presence of mAb W6/32 (50 µg/ml), cetuximab (10 µg/ml) or combination of mAb W6/32 plus cetuximab. The ratio of NK cell cytotoxicity against untreated HNC targets, and IFNγ-treated HNC targets is shown. Results represent mean +/− SEM from three independent experiments. (*P≤0.05, **P≤0.001, ***P≤0.0001)