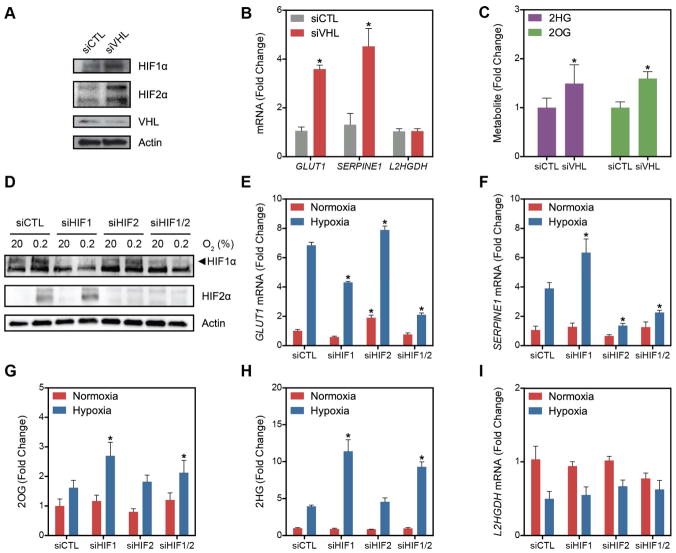
Figure 4. Role of HIF in 2HG Metabolism.
(A) Immunoblot of LF treated with siRNA targeting VHL mRNA compared to siCTL demonstrating stabilization of HIF1α and HIF2α in normoxia. (B) Normoxic stabilization of HIF1α and HIF2α increases GLUT1 and SERPINE1 mRNA, but has no effect on L2HGDH mRNA. (C) HIF stabilization through VHL knockdown is sufficient to increase 2HG and 2OG in normoxia. (D) Immunoblot demonstrating effective knockdown of HIF1α and HIF2α in normoxia and hypoxia. (E) Silencing HIF1α blunts the hypoxia-mediated increase in GLUT1 expression. (F) Silencing HIF2α blunts the hypoxia-mediated increase in SERPINE1 expression. (G and H) 2HG and 2OG in cells treated with HIF siRNA in normoxia and hypoxia. (I) Levels of L2HGDH mRNA in cells treated with siRNA targeting hypoxia-regulated transcription factors. Data are mean ± SEM. See also Figure S4.