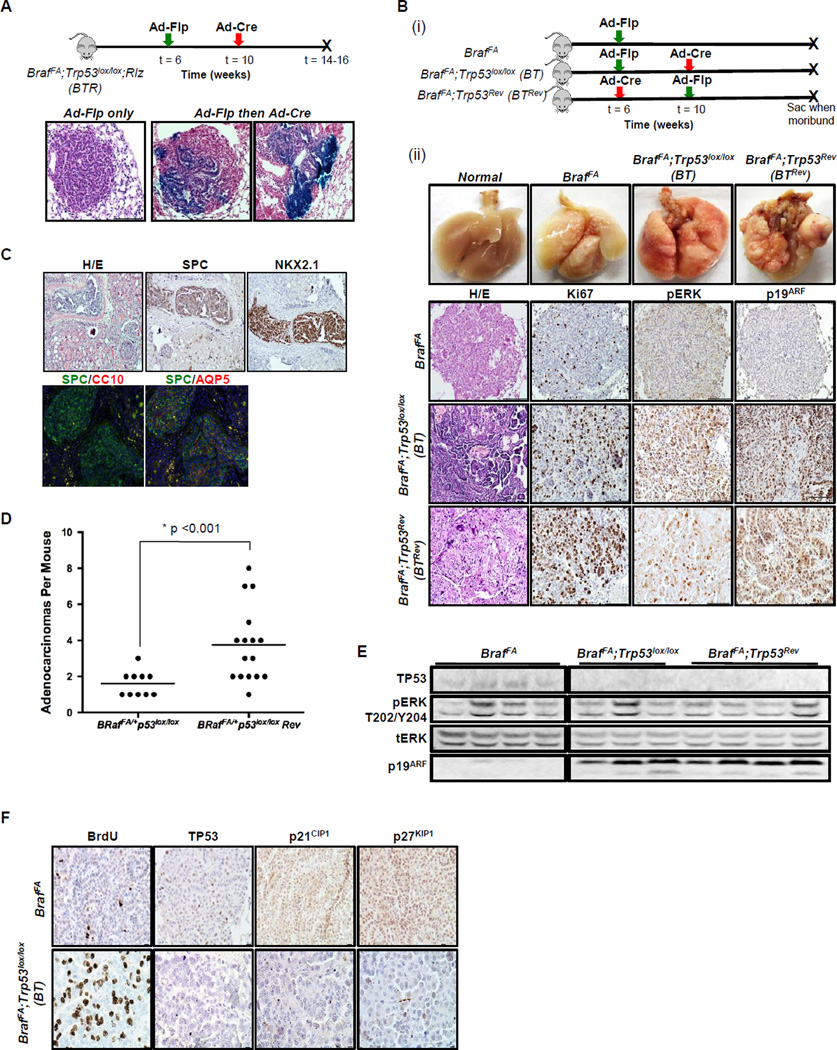
Figure 2. Temporal dissociation of BRAFV600E expression from additional genetic events.
A. Lung infection schematic of BrafFA;Trp53lox/lox; Rlz (BTR) mice to test the efficiency of Ad-Cre mediated recombination in established BRAFV600E-driven tumors initiated with Ad-Flp. Below are H&Es stained with β-galactosidase.
B. (i) Schematic of infection (ii) Comparison of temporal separation of TP53 silencing and BRAFV600E activation to BRAFV600E alone using two infection strategies. 1st row, photographs of the macro lung. 2nd–4th rows, paraffin lung sections of BrafFA, BT and BrafFA; Trp53Rev (BTRev) stained with H&E, Ki67, pERK, and p19ARF to compare proliferation and MAPK signaling.
C. Paraffin sections of a kidney metastasis detected in a BTRev mouse stained with H&E, SPC, NKX2.1, CC10 and AQP5 by IHC and IF.
D. Dot plot showing the average number of lung adenocarcinomas in BT or BTRev mice in which BRAFV600E was activated either prior to or after silencing of TP53.
E. Immunoblot analysis of BRAFV600E or BRAFV600E/TP53Null lung tumor lysates as indicated.
F. Sections of lung tumors from BrafFA or BT mice were stained to detect BrdU incorporation or for expression of TP53, p21CIP1 or p27KIP1 as indicated.