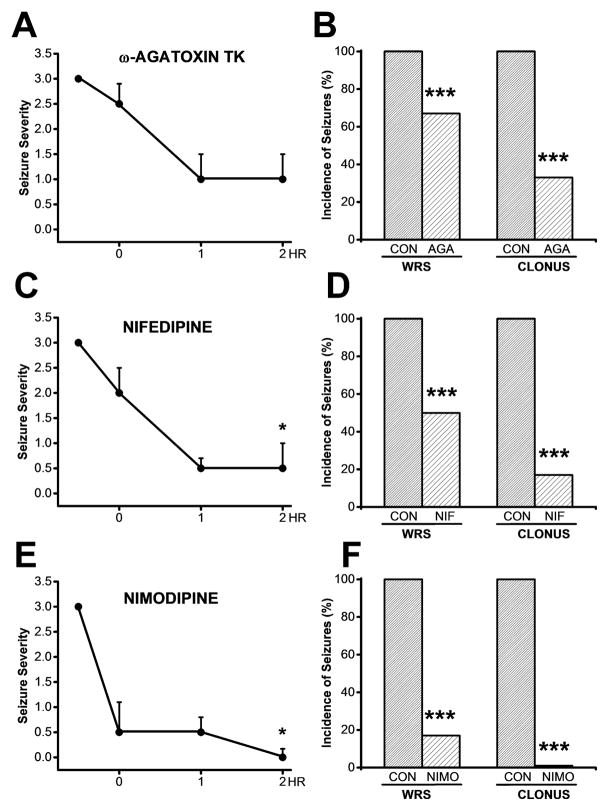
Figure 5.
Effects of bilateral microinjection of CaV1 channel blockers into the IC on the susceptibility to acoustically evoked seizures following ethanol withdrawal. A. The time course of the effects of bilateral microinjections of ω-agatoxin TK (30 nM/side) showed no significant reduction in the median score of seizure severity from 3 to 2.5, 1 and 1at 0.5, 1 and 2 h post infusion, respectively, compared to pre-infusion (n=6, P<0.2, Kruskal Wallis test). B. Microinjection of ω-agatoxin TK significantly reduced the incidence of WRS and clonus by 33% (P<0.001, χ2) and 67% (P<0.001, χ2), respectively, by 2 h post-infusion during the ethanol withdrawal period compared with pre-infusion. C. The time course of the effects of bilateral microinjections of nifedipine (10 μM/side) showed a significant reduction of the median score of seizure severity from 3 to 2, 0.5 and 0.5 at 0.5, 1 and 2 h post-infusion compared to pre-infusion (n=6, P<0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test). D. Bilateral microinjections of nifedipine significantly reduced the occurrence of WRS and clonus by 50% (P<0.001, χ2) and 83% (P<0.001,, χ2), respectively, by 2 h post-infusion during the ethanol withdrawal. E. The time course of the effects of bilateral microinjections of nimodipine (1 μM/side) showed a suppression of the median score of seizure severity from 3 to 0.5, 0.5 and 0 at 0.5, 1, and 2 h post-infusion during ethanol withdrawal (n=6, P<0.05, Kruskal Wallis test). F. Microinjection of nimodipine significantly reduced the occurrence of WRS (n=6, P<0.001, χ2) and completely suppressed the occurrence of clonus (n=6, P<0.001, χ2) at 2 h post-infusion during the ethanol withdrawal period. Each point and bar graph represents the mean± S.E.M and percentage (%), respectively. *P<0.05, ****P<0.001.