Figure 1. Eukaryotic replicative helicase and DNA damage checkpoint activation.
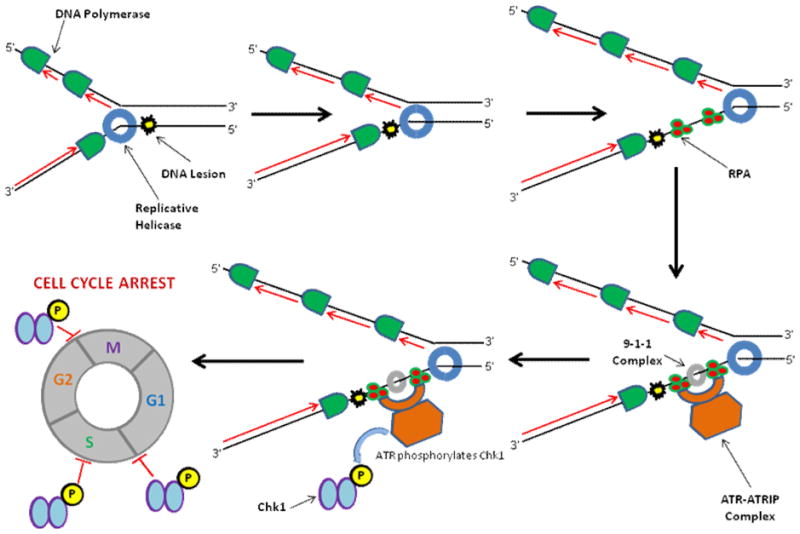
The eukaryotic replicative MCM helicase complex is able to unwind past a DNA lesion at the replication fork. The adduct blocks DNA synthesis catalyzed by a trailing replicative DNA polymerase, leading to the generation of single-stranded DNA which is coated by RPA. The ATRIP/ATR complex and other factors are recruited to the site of replication stress, where ATR is activated and can phosphorylate Chk1, leading to cell cycle arrest.
