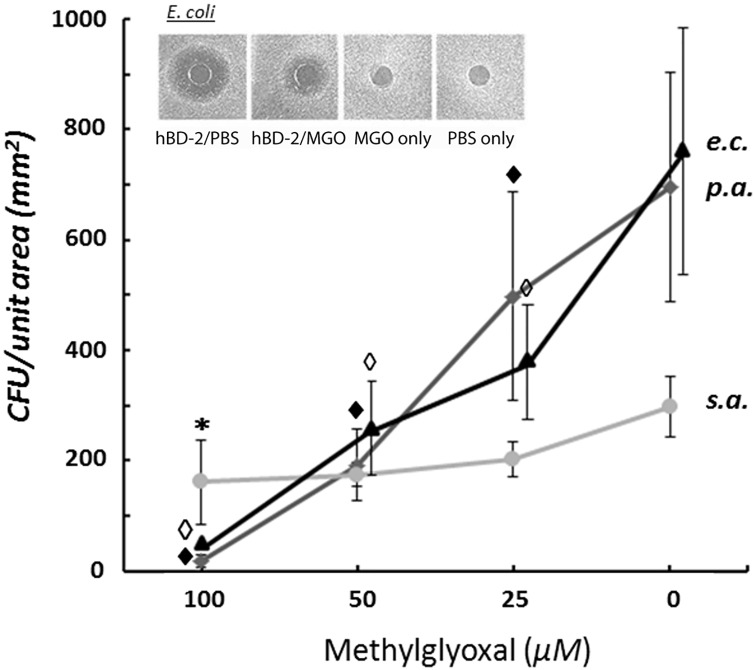
Fig 4. MGO-adducted rhBD-2 shows a concentration-dependent reduction of bactericidal activity, shown as a reduction in CFU vs unadducted peptide.
CFU within a defined area were counted following radial diffusion assays performed with gram-negative, facultative anaerobes Escherichia coli (e.c.) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (p.a.), and with the gram-positive, facultative anaerobe Staphylococcus aureus (s.a.) exposed to 0.5 μg/5 μl with or without MGO. Wild-type hBD-2 is highly bactericidal against most gram-negative bacterial strains, including E. coli, but this function is dramatically reduced following 72 h incubation of rhBD-2 (0.5 μg/5 μl) with 100 μM MGO at 37°C (inset). MGO (100 μM) also reduces rhBD-2 bactericidal function against the gram-positive S. aureus strain. Data is presented as the Mean ± S.D. for N = 5 (e.c.) or N = 6 experiments (p.a., s.a.). Graph line for e.c. is offset slightly for clarity. (♦, ◊: p = 0.01; *: p = 0.05).