Abstract
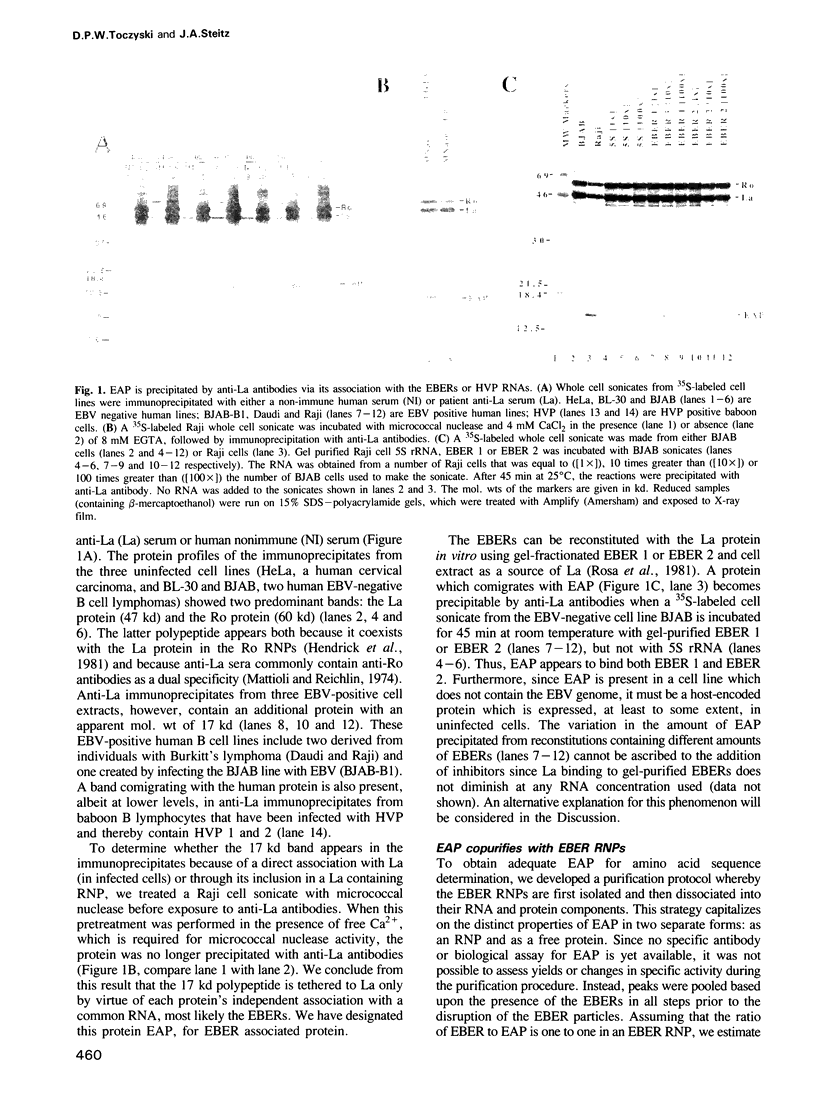
Human B lymphocytes latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) synthesize very large amounts (5 x 10(6)/cell) of two small nuclear RNAs called EBERs (Epstein-Barr encoded RNAs). These RNAs are of unknown function and, like many RNA polymerase III (Pol III) transcripts, bind the La autoantigen. We have discovered that the EBERs also associate with a second highly abundant host-encoded protein designated EAP (EBER associated protein). Human EAP is a small (14,777 dalton, 128 amino acid) polypeptide that binds both EBER 1 and EBER 2. EAP is also found in association with one or both of two analogous virally-encoded RNAs found in baboon cells infected with herpesvirus papio (HVP). We have devised a purification procedure for EAP and have cloned its cDNA from a human placental cDNA library using amino acid sequence data and the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The predicted amino acid sequence of EAP shows a strong resemblance (77% identity) to an endodermal, developmentally regulated sea urchin protein called 217 (Dolecki et al., 1988). EAP contains a potential nuclear localization signal and a highly acidic carboxy terminus, but does not display marked similarity to any other RNA binding proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aota S., Gojobori T., Ishibashi F., Maruyama T., Ikemura T. Codon usage tabulated from the GenBank Genetic Sequence Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r315–r402. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Thimmappaya B. Construction and analysis of additional adenovirus substitution mutants confirm the complementation of VAI RNA function by two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.750-756.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. C., Kenan D., Martin B. J., Keene J. D. Genomic structure and amino acid sequence domains of the human La autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18043–18051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng J. S., Takasaki Y., Tan E. M. Nonhistone nuclear antigens reactive with autoantibodies. Immunofluorescence studies on distribution in synchronized cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):654–660. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolecki G. J., Lum R., Humphreys T. A gene expressed in the endoderm of the sea urchin embryo. DNA. 1988 Nov;7(9):637–643. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald S., van Santen V., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequence of an mRNA transcribed in latent growth-transforming virus infection indicates that it may encode a membrane protein. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.411-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A. M., Mathews M. B. Interaction between VA RNA and the lupus antigen La: formation of a ribonucleoprotein particle in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6772–6776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fregien N., Dolecki G. J., Mandel M., Humphreys T. Molecular cloning of five individual stage- and tissue-specific mRNA sequences from sea urchin pluteus embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1021–1031. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. The RNA binding protein La influences both the accuracy and the efficiency of RNA polymerase III transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wolin S. L., Rinke J., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Ro small cytoplasmic ribonucleoproteins are a subclass of La ribonucleoproteins: further characterization of the Ro and La small ribonucleoproteins from uninfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1138–1149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Shu M. D. Epstein-Barr virus small RNA (EBER) genes: unique transcription units that combine RNA polymerase II and III promoter elements. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90797-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Steitz J. A. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jat P., Arrand J. R. In vitro transcription of two Epstein-Barr virus specified small RNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3407–3425. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., DeCorato D., Safer B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Adenovirus VAI RNA complexes with the 68 000 Mr protein kinase to regulate its autophosphorylation and activity. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):689–697. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurilla M. G., Keene J. D. The leader RNA of vesicular stomatitis virus is bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90541-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazinski D., Grzadzielska E., Das A. Sequence-specific recognition of RNA hairpins by bacteriophage antiterminators requires a conserved arginine-rich motif. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90882-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. I., Murthy S. C., Trimble J. J., Desrosiers R. C., Steitz J. A. Four novel U RNAs are encoded by a herpesvirus. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):599–607. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Andrews N. C., Miller G., Steitz J. A. Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.6164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Kieff E. A second Epstein-Barr virus membrane protein (LMP2) is expressed in latent infection and colocalizes with LMP1. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2319–2326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2319-2326.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marschalek R., Amon-Böhm E., Stoerker J., Klages S., Fleckenstein B., Dingermann T. CMER, an RNA encoded by human cytomegalovirus is most likely transcribed by RNA polymerase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):631–643. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli M., Reichlin M. Heterogeneity of RNA protein antigens reactive with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Description of a cytoplasmic nonribosomal antigen. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jul-Aug;17(4):421–429. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Interaction of adenovirus VA RNAl with the protein kinase DAI: nonequivalence of binding and function. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):843–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90194-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W., Davies M. V., Kelleher K., Kaufman R. J. Cloning and expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4B cDNA: sequence determination identifies a common RNA recognition motif. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2783–2790. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07466.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland R. B., Langevin G. L., Singer R. H., Garcea R. L., Hereford L. M. Amino acid sequences that determine the nuclear localization of yeast histone 2B. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4048–4057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Deng J. S., Stenberg R. M., Tan E. M. Characterization of a phosphoprotein associated with the SS-B/La nuclear antigen in adenovirus-infected and uninfected KB cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1235–1245. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost T. T. Subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Mar;72(3):110–113. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12530348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich P. R., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. RNA of low molecular weight in KB cells infected with adenovirus type 2. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;17(2):428–439. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel P. A., Merrick W. C., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. Regulation of a protein synthesis initiation factor by adenovirus virus-associated RNA. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):196–200. doi: 10.1038/313196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Steitz J. A. Precursor molecules of both human 5S ribosomal RNA and transfer RNAs are bound by a cellular protein reactive with anti-La lupus antibodies. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa M. D., Gottlieb E., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Striking similarities are exhibited by two small Epstein-Barr virus-encoded ribonucleic acids and the adenovirus-associated ribonucleic acids VAI and VAII. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):785–796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Weinberger C., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA facilitates the initiation of translation in virus-infected cells. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Mariano T. M., Reichel P. A., Mathews M. B. Translational control by adenovirus: lack of virus-associated RNAI during adenovirus infection results in phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2 and inhibition of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Williams D. G., Venables P. J., Maini R. N. Monoclonal antibodies to the Sjögren's syndrome associated antigen SS-B (La). J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 28;77(1):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E. Purified lupus antigen La recognizes an oligouridylate stretch common to the 3' termini of RNA polymerase III transcripts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H., Pettersson U., Vennström B., Philipson L., Mathews M. B. A new species of virus-coded low molecular weight RNA from cells infected with adenovirus type 2. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weinberger C., Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA is required for efficient translation of viral mRNAs at late times after infection. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Hastings J. R., Johns E. W. A novel continuous sequence of 41 aspartic and glutamic residues in a non-histone chromosomal protein. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):281–282. doi: 10.1038/271281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Lee S. I., Steitz J. A. Nucleotide sequence of HSUR 5 RNA from herpesvirus saimiri. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1258–1258. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. C., Dixon G. H. Amino acid sequence homologies between the high-mobility-group proteins, HMG-T from trout testis and HMG-1 and -2 from calf thymus: is the poly-aspartic-glutamic acid polypeptide within the main chain? Biosci Rep. 1981 Feb;1(2):167–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01117014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eekelen C., Buijtels H., Linné T., Ohlsson R., Philipson L., van Venrooij W. Detection of a cellular polypeptide associated with adenovirus-coded VA RNA using in vitro labeling of proteins cross-linked to RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3039–3052. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA VII: size and direction of transcription of virus-specified cytoplasmic RNAs in a transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]