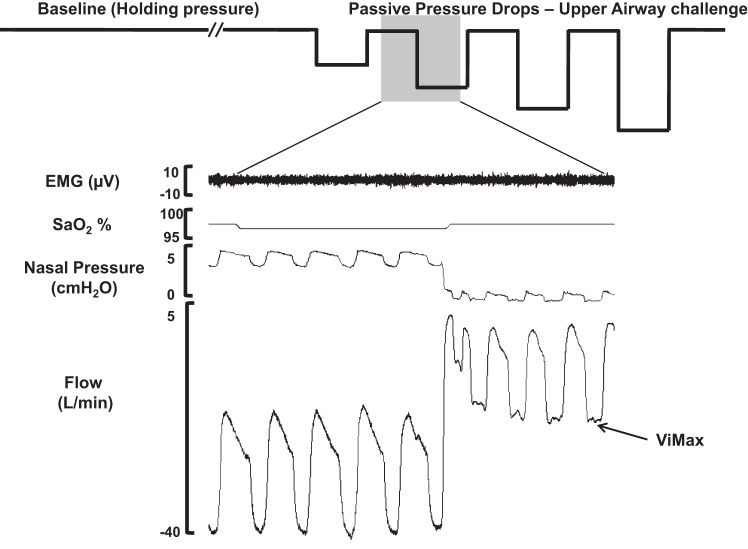
Fig. 1.
Experimental protocol. Schematic diagram of the experimental protocols (top) and polysomnographic responses (bottom) during non-rapid eye movement sleep in an apneic male subject. Baseline (left): nasal pressure was adjusted to effective continuous positive airway pressure and held for at least 3 min (holding pressure) to establish a stable non-flow-limited breathing pattern (see flow trace, bottom left). Passive upper airway obstruction (middle left): a series of brief (5 breaths) drops in nasal pressure from holding pressure were performed without concomitant activation of EMG. During these drops, upper airway obstruction ensued, as indicated by inspiratory flow limitation as in the flow trace below. SaO2, arterial O2 saturation; Vimax, maximal inspiratory flow.