Fig. 2.
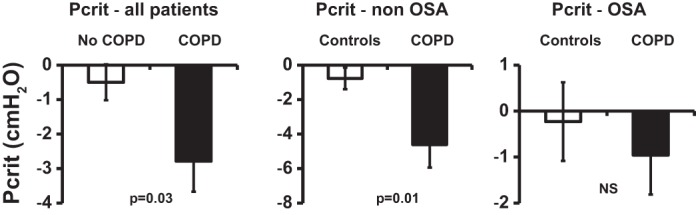
Passive critical closing pressure (Pcrit) measurements in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients and controls. The graph represents average passive Pcrit values for COPD patients and matched controls. Left: all patients. Middle: non-obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) patients. Right: OSA patients. Values are means ± SE. Upper airway collapsibility (passive Pcrit) is lower in patients with COPD compared with subjects matched for age, sex, body mass index, and respiratory disturbance index (P = 0.03). This difference seems greater in nonapneic patients, but can no longer be noticed in apneic patients. NS, nonsignificant.
