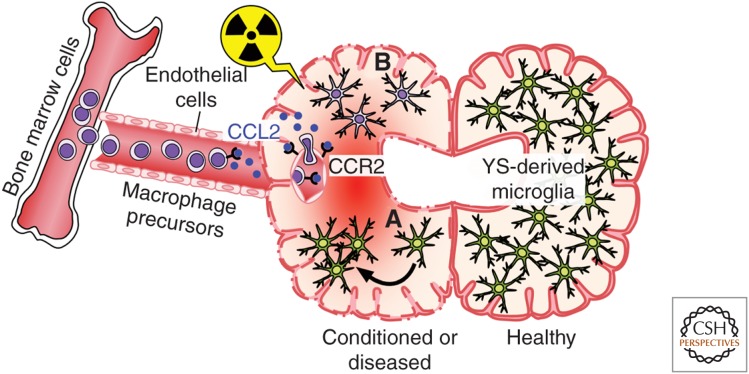
Figure 3.
Formation of BM-derived microglia in the adult mouse brain. Postnatal BM-derived microglia form only under defined host conditions in the CNS. BM cells (left) are released into the bloodstream in a chemokine receptor (CCR)-2-dependent fashion and may enter the conditioned CNS. Local conditioning of the CNS can occur via irradiation and neurodegeneration, which lead to both disruption of the BBB and induction of chemokines, such as CCL2, thus, allowing engraftment of BM-derived macrophages. (A) YS-derived microglia (green) perform self-renewal by undergoing proliferation (indicated by an arrow), and (B) BM-derived phagocyte (purple).