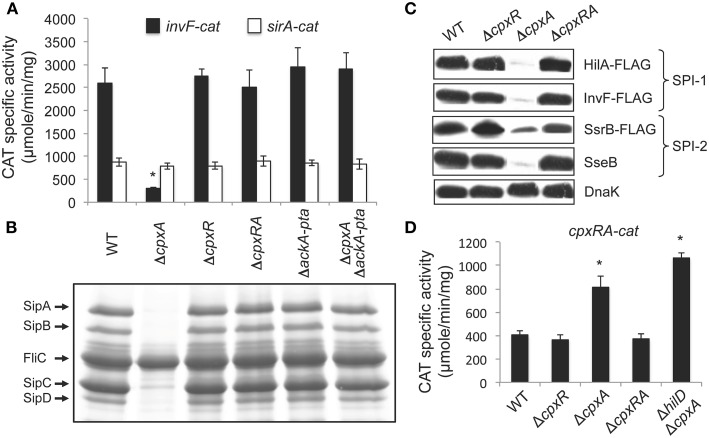
Figure 1.
The absence of CpxA represses SPI-1 genes by the activation of CpxR via the AckA and Pta enzymes. (A) Expression of the invF-cat and sirA-cat transcriptional fusions, carried by plasmids pinvF-cat and psirA-cat, respectively, was tested in the WT S. Typhimurium 14028s strain and its isogenic ΔcpxA, ΔcpxR, ΔcpxRA, ΔackA-pta, and ΔcpxA ΔackA-pta mutants. (B) Secretion analysis of the SPI-1-encoded proteins SipA, SipB, SipC, and SipD was tested in the WT S. Typhimurium strain 14028s and its isogenic ΔcpxA, ΔcpxR, ΔcpxRA, ΔackA-pta, and ΔcpxA ΔackA-pta mutants grown for 9 h in LB medium at 37°C. FliC is a flagellar protein whose secretion is SPI-1-independent. (C) Expression of the SPI-1-encoded HilA-FLAG and InvF-FLAG and the SPI-2-encoded SsrB-FLAG and SseB, in the WT S. Typhimurium strain and its isogenic ΔcpxR, ΔcpxA and ΔcpxRA mutants, carrying the respective chromosomal FLAG-tagged gene, was analyzed by Western blotting using monoclonal anti-FLAG or polyclonal anti-SseB antibodies. Whole cell lysates were prepared from samples of bacterial cultures grown in LB medium at 37°C for 5 or 9 h, for detection of SPI-1- and SPI-2-encoded proteins, respectively. As a loading control, the expression of DnaK was also determined using monoclonal anti-DnaK antibodies. (D) Expression of the cpxRA-cat transcriptional fusion, carried by plasmid pcpxRA-cat, was tested in the WT S. Typhimurium 14028s strain and its isogenic ΔcpxR, ΔcpxA, ΔcpxRA, and ΔhilD ΔcpxA mutants. CAT-specific activity of cat fusions was determined from samples collected of bacterial cultures grown for 5 h in LB medium at 37°C. The data are the averages of three different experiments performed in duplicate. Bars represent the standard deviations. *Expression statistically different with respect to that shown by the same fusion in the WT strain.