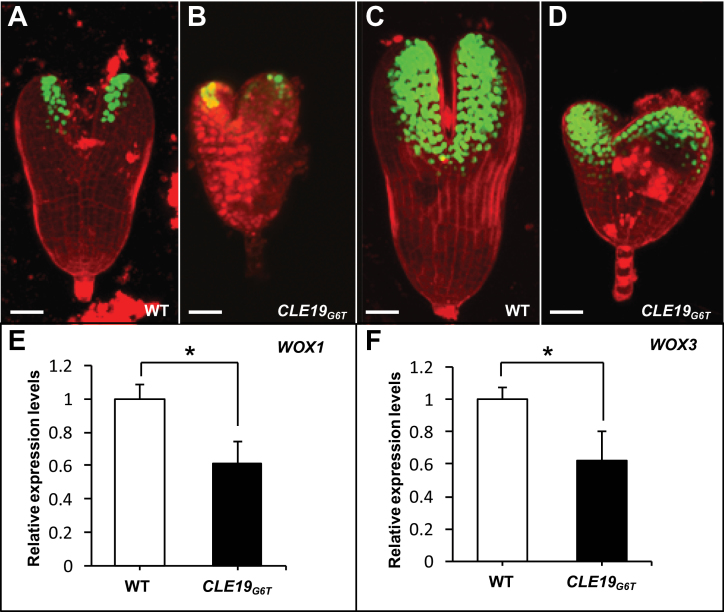
Fig. 5.
Expression of cotyledon-specific genes in arrested embryos from pCLE19:CLE19 G6T :tCLE19 transgenic plants. (A–D) Confocal microscopic examinations of embryos excised from wild-type plants (WT) carrying pWOX1:SV40-3XGFP (A) or pWOX3:SV40-3XGFP marker constructs (C), or from plants carrying pWOX1:SV40-3XGFP/pCLE19:CLE19 G6T :tCLE19 (B) or pWOX3:SV40-3XGFP/pCLE19:CLE19 G6T :tCLE19 double constructs (D). Note that similar GFP expression, though with a reduced level, was observed in cotyledon primordia of arrested embryos from pCLE19:CLE19 G6T :tCLE19 transgenic plants (CLE19 G6T), as compared with embryos from plants carrying only marker constructs (A, C). Scale bars=50 μm. (E, F) qRT-PCR showed reduced levels of WOX1 (E) and WOX3 expression (F) in ovules from the wild type (WT) and pCLE19:CLE19 G6T :tCLE19 transgenic plants (CLE19 G6T). Data represent the mean ±SD from three independently extracted RNA samples. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type (P < 0.01 by Student’s t-test).