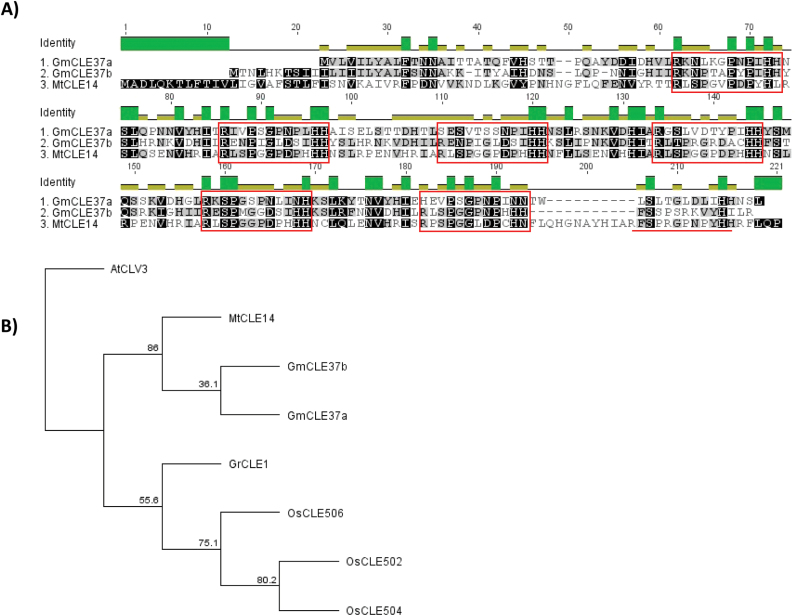
Fig. 4.
Multi-CLE domain pre-propeptides. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of the soybean and M. truncatula multi-CLE domain pre-propeptides, with putative 13 amino acid residue CLE domains highlighted by a red box. An additional CLE domain of MtCLE14 that is not detected in the two soybean pre-propeptides is underlined in red. Four MtCLE14 CLE domains are identical in sequence (CLE domains 2–5) while there are no 100% conserved 13 amino acid residue CLE domains in soybean. However, there are two fully conserved 12 residue CLE domains in GmCLE37b (CLE domains 1 and 2). (B) Phylogenetic tree of known multi-CLE domain-containing pre-propeptides of rice (Oryza sativa), potato cyst nematode (Globodera rostochiensis), MtCLE14 of M. truncatula, and the newly identified GmCLE27a and GmCLE37b of soybean, including AtCLV3 as an outgroup. The multi-CLE domain pre-propeptides identified here cluster separately from those that were previously identified. The tree is shown with bootstrap confidence values expressed as a percentage from 1000 bootstrap replications.